In today’s hyper-competitive supply chain environment, businesses must leverage smart logistics strategies to maintain control over their brand, supplier relationships, and customer experience.
One increasingly popular tactic is blind shipping, also known as a blind shipment. This method is particularly useful for e-commerce companies, wholesalers, drop shippers, and brands that want to preserve supplier anonymity and manage their supply chain control effectively.
This article offers an in-depth explanation of blind shipping, exploring its benefits, challenges, and best practices. Whether you’re a retailer, a freight forwarding agent, or a 3PL (third-party logistics) provider, understanding blind shipments can enhance your operational strategy.
What is Blind Shipping
Blind shipping refers to a shipping method where one or more parties involved in the transaction are unaware of each other’s identities. In a typical blind shipment, the end customer receives the product without knowing the supplier or manufacturer. Conversely, the supplier may not know the end customer.
Blind shipments are often used by resellers who want to hide the origin of goods from their customers. By doing so, they maintain their position in the supply chain and prevent disintermediation, where customers bypass the reseller to deal directly with the supplier.
This process typically requires specialized documentation, coordination with logistics providers, and clear communication with suppliers and carriers to ensure a seamless delivery while preserving supplier anonymity.
How Does Blind Shipping Work
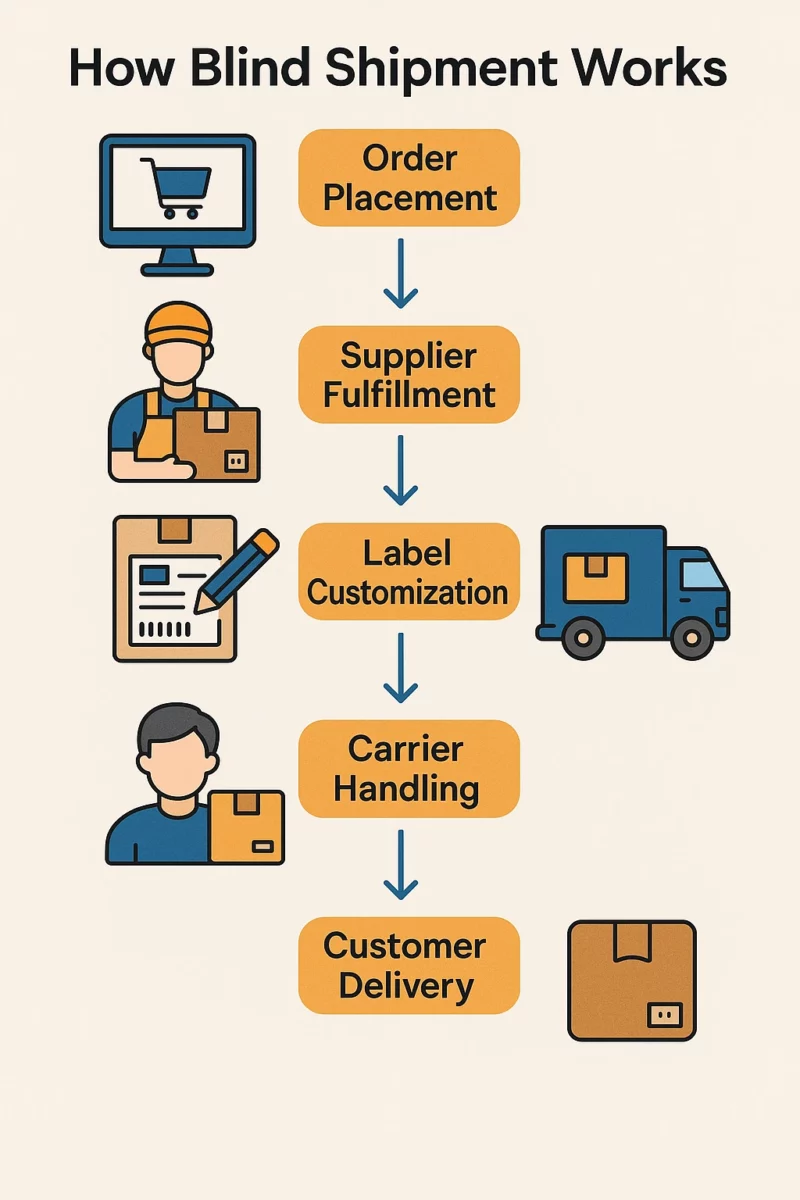
Blind shipping involves coordination among multiple parties: the seller (or intermediary), the supplier, and the carrier. Here’s how it typically works:
- Order Placement: A customer places an order through the seller’s platform.
- Supplier Fulfillment: The seller forwards the order to the supplier or manufacturer for fulfillment.
- Label Customization: Instead of shipping the order with the supplier’s branding, a neutral shipping label is used. This label often displays the seller’s information or no sender details at all.
- Carrier Handling: The supplier ships the product using a third-party carrier that follows specific carrier requirements to maintain anonymity.
- Customer Delivery: The customer receives the package without any clue about the supplier’s identity.
Key Components of a Blind Shipment
Understanding the technical aspects of a blind shipment helps ensure accuracy and efficiency:
- Logo masking/label masking: Crucial for removing the supplier’s branding from the package.
- Freight documentation: Bills of lading and shipping documents must be carefully prepared to ensure correct sender/receiver details.
- Blind Bill of Lading: A specialized type of freight documentation used in blind shipping that conceals the actual shipper or consignee from certain parties to maintain supplier anonymity and brand protection. A blind bill of lading may show the reseller’s information instead of the true origin to protect the brand and prevent disintermediation.
- Carrier requirements: Some carriers have strict protocols for handling blind shipments. These may include sealed documents, pre-approved shipping labels, and exact instructions on delivery paperwork.
- Accessorial charges: Extra fees may apply for services like re-labeling, documentation handling, or special routing. It’s essential to anticipate these additional carrier fees in advance.
Types of Blind Shipping
There are several variations of blind shipping depending on how many parties are kept unaware of each other. Understanding these variations is crucial for implementing the right level of discretion and control.
Single Blind Shipment
In this model, either the shipper or the consignee is unaware of the other party. Typically, the end customer doesn’t know who the original supplier or manufacturer is. This is the most common form used in e-commerce and drop shipping.
Double Blind Shipment
Both the supplier and the end customer are blind to each other’s identity. A freight forwarding agent or 3PL is usually the intermediary, managing communication and carrier handling. This is ideal for sellers working with sensitive markets or niche manufacturers.
Triple Blind Shipment
This advanced method ensures that the supplier, customer, and even the carrier are unaware of each other’s full identities. Specialized systems and freight documentation, such as encrypted blind bills of lading, are used. Neutral shipping facilities may be involved to repackage and reassign tracking information.
Custom Blind Shipping
Some businesses implement a tailored form of blind shipment where only partial information is shared with selected logistics partners. This ensures brand protection while meeting internal compliance needs.
Each type serves a different business model and must be assessed based on the level of confidentiality required, the capability of 3PL providers, and the carrier requirements involved.
Benefits of Blind Shipping
Blind shipping provides significant advantages for both resellers and customers:
1. Supplier Anonymity
Keeping the supplier’s identity confidential protects sourcing channels and gives sellers a competitive edge.
2. Supply Chain Control
Control over packaging, labeling, and the shipping process helps businesses maintain brand consistency and reduce leakage of operational details.
3. Disintermediation Prevention
By obscuring the supplier’s identity, businesses prevent customers from bypassing intermediaries and going straight to the source.
4. Brand Protection
Logo masking/label masking enables companies to maintain a cohesive brand image and retain full credit for customer satisfaction.
5. Operational Efficiency
Streamlining operations through experienced freight forwarding partners or 3PL (third-party logistics) services enables rapid fulfillment while ensuring sensitive information remains confidential.
6. Market Flexibility
Businesses can source from multiple vendors without customers detecting variations in origin or quality, giving them more room to negotiate pricing and diversify inventory.
Challenges of Blind Shipments
While beneficial, blind shipping also presents several challenges:
1. Complex Freight Documentation
The need to anonymize documents like the bill of lading and packing slips demands careful planning. Mistakes can reveal identities and void the purpose of blind shipping.
2. Carrier Handling Issues
Not every carrier is equipped or willing to follow the strict protocols of a blind shipment. Choosing experienced freight forwarding agents who can manage these processes is essential.
3. Accessorial Charges
Blind shipping often includes accessorial charges such as re-labeling, document sealing, and indirect routing. These extra costs can reduce profit margins if not managed.
4. Limited Returns Management
Returns become more complicated as blind shipping obscures the true return address. Many companies rely on 3PL partners or reverse logistics systems to handle these challenges.
5. Compliance Risks
Improper handling of customs forms, freight documentation, or shipping labels may lead to legal penalties or lost shipments.
Role of 3PL and Freight Forwarding Services
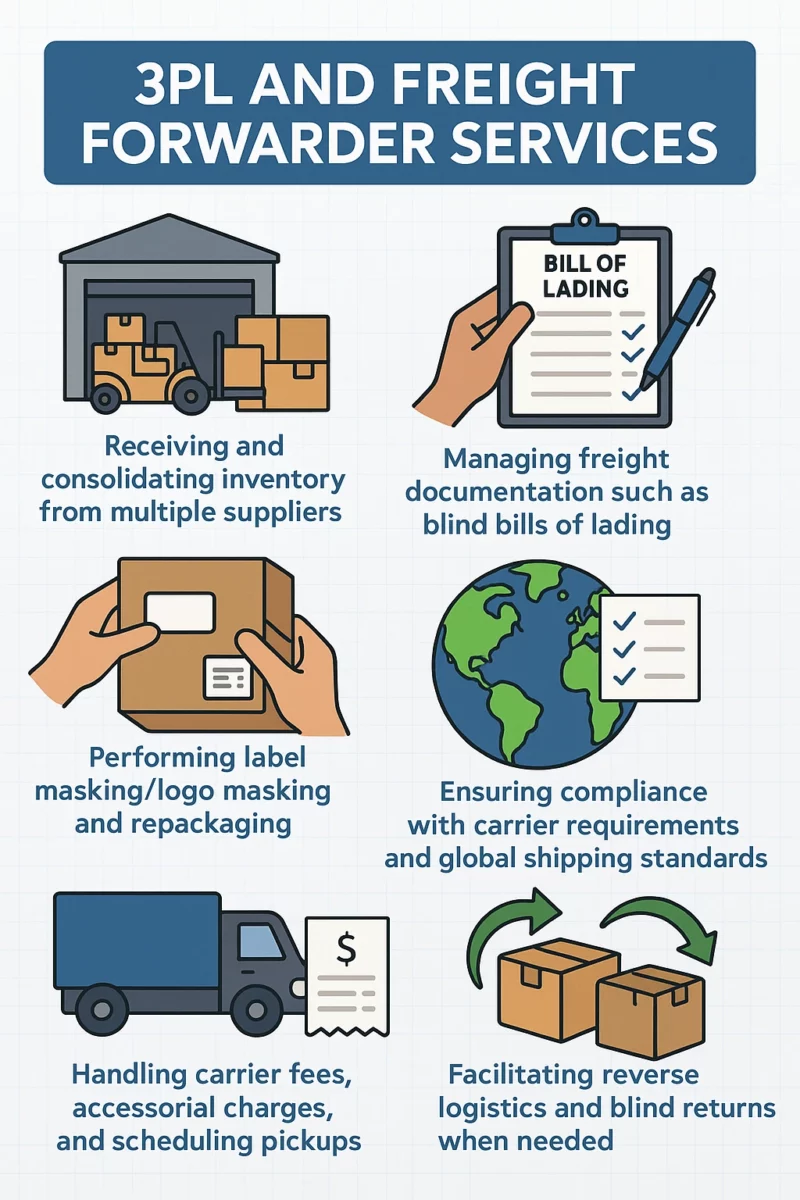
3PL (third-party logistics) providers and freight forwarding companies play a critical role in executing blind shipments effectively. Their services include:
- Receiving and consolidating inventory from multiple suppliers
- Performing label masking/logo masking and repackaging
- Managing freight documentation such as blind bills of lading
- Ensuring compliance with carrier requirements and global shipping standards
- Handling carrier fees, accessorial charges, and scheduling pickups
- Facilitating reverse logistics and blind returns when needed
Experienced 3PLs act as a shield between the supplier and the buyer, preserving supplier anonymity and offering transparency to the seller without revealing internal logistics details.
Best Practices for Blind Shipping
To ensure your blind shipping process runs efficiently, consider the following best practices:
1. Vet Your Carriers and 3PL Partners
Choose carriers and 3PL providers with a proven track record of executing blind shipments according to exact specifications and handling sensitive documentation.
2. Standardize Freight Documentation
Use templated blind bills of lading and ensure they’re adapted for every carrier. Avoid common pitfalls like incorrect return addresses or traceable codes.
3. Streamline Communication
Keep communication centralized to reduce errors and information leaks. Let your freight forwarding partner handle coordination.
4. Integrate Tracking Systems
Modern logistics platforms enable anonymous tracking, allowing you to monitor shipments without exposing customer or supplier information.
5. Anticipate Accessorial Charges
Factor in possible accessorial charges such as storage, repackaging, and non-standard delivery options to protect your margins.
6. Maintain Compliance Records
Log and archive all shipping documentation to demonstrate compliance with customs and regulatory requirements.
Real-World Example
Imagine an online electronics retailer that sources gadgets from various Asian manufacturers. The retailer wants to ensure customers never know the origin of the products to avoid losing them to direct manufacturers.
Using a blind shipment process, the retailer:
- Places orders with the supplier.
- Sends custom packaging instructions to their 3PL provider.
- Ensures all freight documentation, including a blind bill of lading, lists the retailer as the shipper.
- Uses neutral shipping labels to eliminate manufacturer branding.
- Coordinates with a trusted carrier familiar with carrier requirements and ready to manage any accessorial charges.
The customer receives a seamless brand experience, unaware of the back-end logistics.
Conclusion
In a rapidly evolving supply chain environment, blind shipping offers a strategic advantage for companies seeking to protect their supply sources, reinforce their branding, and enhance customer loyalty. While it requires additional coordination and can incur carrier fees or accessorial charges, the benefits of supplier anonymity, disintermediation prevention, and brand protection make blind shipments a valuable tool in modern logistics.
By understanding the components, challenges, and best practices of blind shipping, businesses can execute this strategy effectively and sustainably. With the right partners and protocols in place, blind shipments can be a seamless and scalable component of your supply chain, all while safeguarding critical commercial relationships and elevating the end-customer experience.
FAQs
An example of a blind shipment is when an online retailer purchases goods from a manufacturer but ships them directly to the end customer using a neutral shipping label that hides the manufacturer’s identity. The customer receives the product without knowing the original source.
While both methods involve direct shipment from supplier to customer, blind shipping specifically conceals the identity of the supplier. Drop shipping may or may not involve such concealment, depending on the arrangement and shipping documents used
Not all carriers are equipped or willing to manage blind shipments. Many have specific carrier requirements and may charge accessorial fees for services like label masking or special freight documentation. It’s essential to work with carriers and 3PLs experienced in blind shipping.
Yes, blind shipments often incur additional costs, known as accessorial charges. These can include fees for re-labeling, repackaging, document processing, and neutral shipping requirements. Always confirm these with your carrier or 3PL provider.
Yes, blind shipping is legal, provided all freight documentation is accurate and compliant with shipping regulations. The process must not involve false declarations or misrepresentation of goods.