In the ever-evolving landscape of commerce, particularly e-commerce shipping, businesses face a critical logistical decision: should they rely on bulk shipping or process individual orders? The financial implications of each approach can significantly impact your bottom line. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the pros and cons of both models, offer a detailed shipping cost analysis, and explore factors like economies of scale, inventory management, and order fulfillment strategies to determine which option saves more money.
Understanding Bulk Shipping vs. Individual Orders
Bulk Shipping
Bulk shipping involves sending large quantities of goods in a single shipment. This approach is commonly used in B2B settings, wholesale distribution, or when businesses restock inventory at retail locations. The idea is simple: consolidate items to lower freight consolidation costs and improve logistics efficiency.
Individual Orders
On the other hand, individual order shipping involves processing and shipping items on a per-customer basis. This model is prevalent in direct-to-consumer e-commerce platforms. While it offers high flexibility and quick delivery, it often comes with increased costs due to repetitive processing, packaging, and shipping.
Shipping Cost Analysis: Which is More Economical?
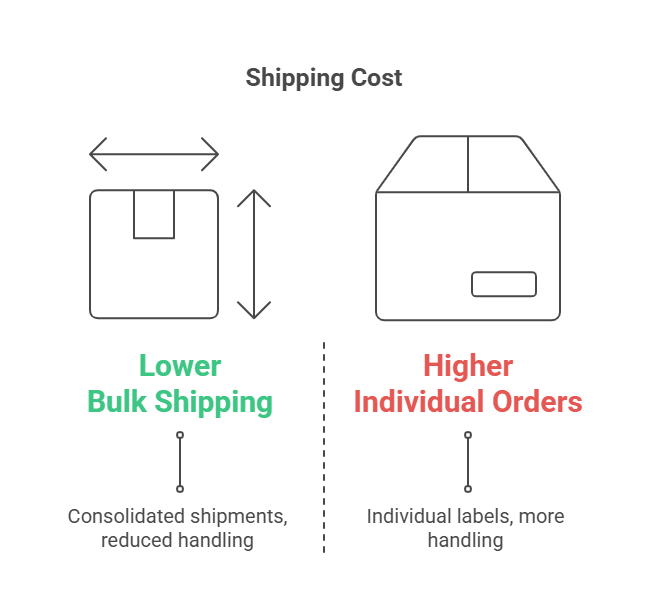
One of the primary reasons companies opt for bulk shipping is to reduce the cost per unit of shipping. This is where economies of scale come into play. The more you ship at once, the lower your cost per item.
Bulk Shipping
- Lower Shipping Rates: Shipping larger volumes allows you to negotiate better rates with freight carriers.
- Fewer Trips, Less Fuel: Consolidated shipments reduce the number of trips required, saving on fuel and labor.
- Reduced Packaging Costs: Bulk shipments often require less packaging per unit compared to individual packages.
Individual Orders
- Higher Unit Costs: Each package needs individual labels, packing materials, and handling time.
- Carrier Charges: Most carriers charge a base rate per package, which adds up quickly with multiple shipments.
- Returns Management: Handling returns from individual shipments can add to the cost and complexity.
Verdict:
From a pure shipping cost analysis standpoint, bulk shipping usually wins due to freight consolidation and reduced handling.
Inventory Management Considerations
Shipping strategy doesn’t just affect transport, it also influences inventory management.
Bulk Shipping
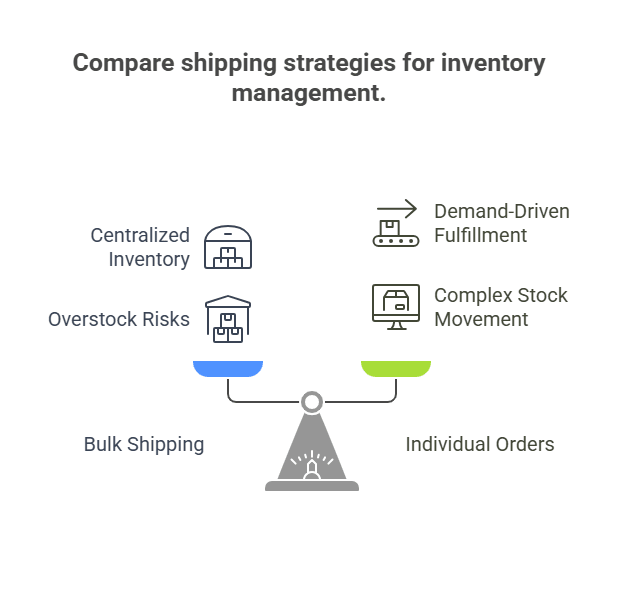
- Centralized Inventory: With bulk shipping, businesses can maintain stock at centralized locations, which simplifies tracking and forecasting.
- Overstock Risks: However, bulk shipments might lead to overstocking if demand is overestimated.
Individual Orders
- Demand-Driven Fulfillment: You ship as orders come in, reducing the risk of overstocking.
- Complex Stock Movement: More dynamic, but can create challenges with tracking inventory across multiple locations.
Verdict:
Bulk shipping provides stability and predictability in inventory management, while individual orders offer flexibility but require more sophisticated tracking systems.
Order Fulfillment Strategies and Logistics Efficiency
Order fulfillment strategies need to align with your shipping model to ensure timely and cost-effective delivery.
Bulk Shipping
- Streamlined Processes: Bulk shipping simplifies fulfillment through large, planned shipments.
- Warehouse Efficiency: Fewer pick-and-pack operations translate to better use of labor and equipment.
Individual Orders
- Customizable Fulfillment: Ideal for personalized or made-to-order products.
- High Labor Costs: Increased picking, packing, and processing requirements per order can slow down operations.
Verdict:
Bulk shipping often leads to higher logistics efficiency, especially when labor and warehouse resources are limited.
Supply Chain Optimization
Shipping strategy plays a pivotal role in overall supply chain optimization. It affects how quickly and effectively you can respond to demand fluctuations and supply disruptions.
Bulk Shipping
- Long-Term Planning: Ideal for predictable supply chains with established demand patterns.
- Lead Time Risks: Long lead times can be problematic if customer needs shift suddenly.
Individual Orders
- Agile Supply Chain: You can respond faster to market changes.
- Higher Operational Complexity: Managing many small shipments requires advanced supply chain coordination.
Verdict:
If your business benefits from stability and predictability, bulk shipping is advantageous. If you operate in a fast-changing market, the agility of individual orders might be worth the cost.
Packaging Solutions and Sustainability
Environmental and economic considerations around packaging can also sway your decision.
Bulk Shipping
- Less Packaging Waste: Fewer materials are used per item shipped.
- Lower Packaging Costs: Economies of scale in packaging materials procurement.
Individual Orders
- High Packaging Needs: Each order requires individual packaging.
- Sustainability Concerns: More materials and waste generation.
Verdict:
From both a cost and environmental standpoint, bulk shipping tends to offer superior packaging solutions.
Warehouse Storage Costs
Another hidden factor in the bulk shipping vs. individual orders debate is warehouse storage costs.
Bulk Shipping
- More Inventory On Hand: You’ll need more warehouse space to store large incoming shipments.
- Lower Handling Costs: Fewer stock-ins and stock-outs mean less wear on staff and equipment.
Individual Orders
- Lean Inventory: Less space needed as inventory is more closely aligned with real-time demand.
- High Turnover Pressure: Fast inventory movement demands a highly organized and responsive system.
Verdict:
Bulk shipping may incur higher warehouse storage costs, but those may be offset by savings in labor and reduced handling needs.

Real-World Examples
Example 1: A Wholesale Business
A company selling electronics components to retailers across the country uses bulk shipping. They send monthly pallets to retail partners, significantly cutting down on transportation and packaging costs. Their order fulfillment strategy is synchronized with production cycles, resulting in minimal downtime and supply chain optimization.
Example 2: A Direct-to-Consumer Brand
An online skincare brand processes thousands of individual orders daily. Their focus is customer satisfaction and personalization, which justifies the higher shipping and packaging costs. However, they invest in automated warehousing and fulfillment systems to maintain logistics efficiency and reduce errors.
When to Choose Bulk Shipping vs. Individual Orders
Choose Bulk Shipping If:
- You deal in high-volume B2B sales.
- Your demand forecasts are accurate and stable.
- You want to capitalize on economies of scale.
- Storage space and handling costs are manageable.
Choose Individual Orders If:
- You cater directly to consumers with customized or niche products.
- Speed and flexibility are more important than cost savings.
- You have a robust fulfillment system in place.
- Real-time inventory is critical to your operations.
Final Thoughts
So, bulk shipping vs. individual orders: which saves more money? The answer largely depends on your business model, customer base, and operational capacity.
Bulk shipping tends to offer significant cost advantages through freight consolidation, packaging solutions, and logistics efficiency, especially when supported by stable demand and solid inventory management systems.
Individual orders, while potentially more expensive, provide unmatched flexibility and customer satisfaction, key benefits in the era of personalized commerce and next-day delivery expectations.
Ultimately, a hybrid approach, leveraging bulk shipping to fulfillment centers and processing individual orders from there, can often provide the best of both worlds: cost-efficiency and customer satisfaction.
FAQs
Bulk shipping involves consolidating a large number of items into a single shipment, usually for wholesale or restocking purposes. Individual orders are shipped separately to customers, typically in direct-to-consumer e-commerce models.
Generally, bulk shipping is more cost-effective due to economies of scale, reduced freight consolidation costs, and lower packaging expenses. Individual orders offer more flexibility but tend to be more expensive per unit.
Bulk shipping typically requires more warehouse space and ties up inventory in advance. Individual orders allow for leaner inventory management, but require more precise stock tracking and faster turnover.
Not always. While bulk shipping offers cost savings, many e-commerce shipping models rely on individual order fulfillment to meet customer expectations for fast and personalized service.
Freight consolidation combines multiple shipments into one, reducing the cost per unit shipped. This is a key benefit of bulk shipping and contributes to overall logistics efficiency.