If you’re an Indian exporter, the thought of your aromatic turmeric, fiery red chilli, or robust coffee reaching Portuguese markets is exciting. But the European Union isn’t just another market, it’s one of the strictest in the world when it comes to food safety, labelling, and traceability.
Shipping to Portugal means navigating EU contaminants limits for spices (aflatoxin, lead) under Reg. 2023/915, EU pesticide MRLs for tea, coffee, and spices under Reg. 396/2005, and understanding a range of official controls, organic import requirements, and packaging rules.
This guide walks you through every step from sourcing and lab testing in India to official checks at the Portuguese border so your spices, tea, and coffee arrive safely and impress your buyers.

1. Sourcing and Production Where Quality Begins
The first step in a successful export is sourcing high-quality, compliant raw materials.
Contaminants and Heavy Metals
Under EU Regulation 2023/915, the EU sets maximum limits for contaminants like:
- Aflatoxins – especially relevant for turmeric, chilli, and paprika.
- Lead and cadmium – sometimes found in soil or during processing.
- Ochratoxin A – often found in coffee and dried herbs.
Spices and herbs must be stored, dried, and processed under conditions that minimize contamination. Buyers in Portugal are particularly sensitive to aflatoxin levels because the EU enforces strict border checks.
Pesticide Residues
EU pesticide MRLs for spices, tea, and coffee are defined under Reg. 396/2005.
- Each crop has its own maximum allowed pesticide residue.
- If a pesticide doesn’t have a set MRL for a particular commodity, the default 0.01 mg/kg applies.
- Testing your products for compliance before export saves time and avoids border rejections or RASFF notifications.
Pro Tip: Work with NABL-accredited labs and keep all test results handy. Pre-empting potential issues is better than dealing with delays at Portuguese ports.
2. Preparing Your Shipment — Documentation and Packaging
Shipping to Portugal requires complete documentation and compliant packaging.
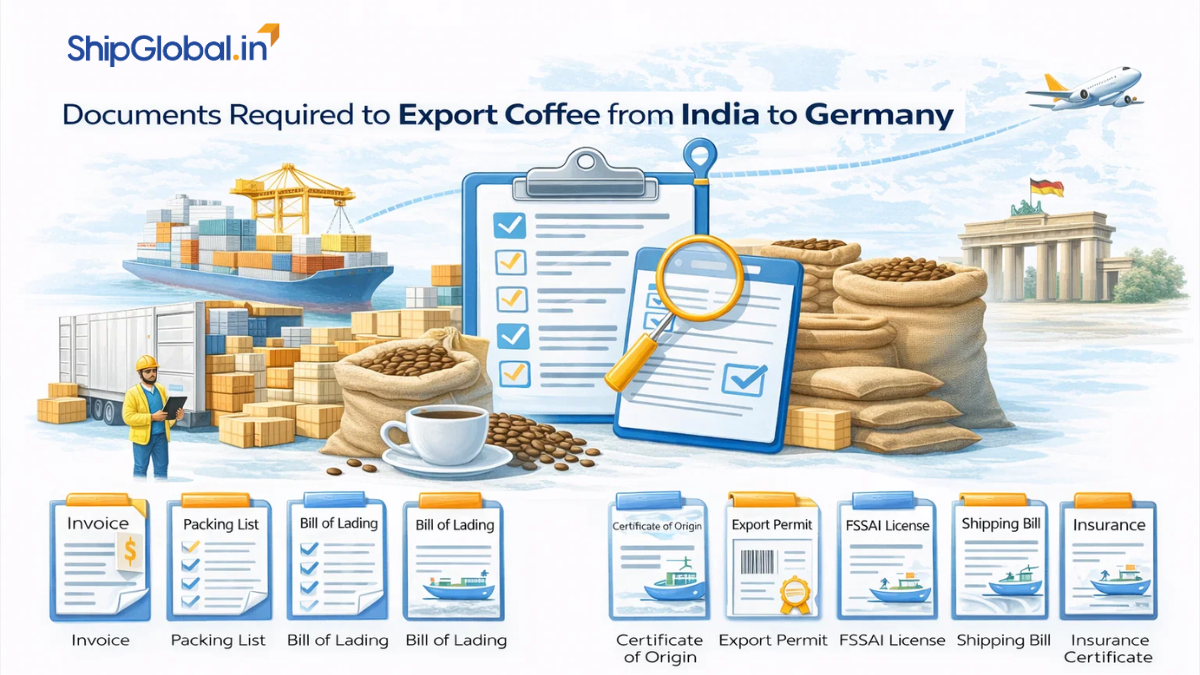
Essential Documents
- Commercial Invoice – includes product name, quantity, price, and HS code.
- Packing List – detailed contents, weights, and package count.
- Certificate of Origin (CoO) – essential for customs and preferential trade arrangements.
- Fumigation or Pest-Free Certificate – for certain spices and coffee beans.
- Phytosanitary Certificate – required for fresh herbs or seeds for sowing, not usually for dried spices.
- Lab Test Certificates – pesticide residues, aflatoxin, ochratoxin, heavy metals.
- Private Standards / Sustainability Certificates – organic, Fairtrade, Rainforest Alliance.
Food Contact Packaging Compliance
EU Regulation 1935/2004 requires all packaging to be safe for food contact. Make sure your:
- Packaging is food-grade and moisture-proof.
- Labels clearly mention product name, lot number, net weight, and “Product of India.”
- Inner and outer packaging protects against contamination during transit.
HS Codes for Spices, Tea & Coffee (TARIC Reference)
| Product category | HS code (heading) | Typical TARIC / subheading (example) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coffee | 0901 | 0901.21 / 0901.22 (green/roasted) | Coffee, whether or not roasted or decaffeinated (green beans or roasted beans). |
| Tea | 0902 | 0902.10 / 0902.20 (black/green; flavoured variants) | Tea, whether or not flavoured (packaged for retail or bulk leaf tea). |
| Pepper (black/white) | 0904 | 0904.11 / 0904.12 (ground/whole) | Pepper of the genus Piper (dried, whole or crushed). |
| Chilli, Capsicum, Pimenta (dried) | 0904 | 0904.20 (dried chillies and cayenne) | Dried chillies, cayenne pepper, paprika (various processed spice forms). |
| Vanilla | 0905 | 0905.00 | Vanilla beans (whole vanilla pods). |
| Cinnamon | 0906 | 0906.11 / 0906.12 | Cinnamon and cinnamon-tree flowers (bark, whole or cut). |
| Cloves | 0907 | 0907.00 | Cloves (whole fruit, cloves and stems). |
| Nutmeg, Mace, Cardamoms | 0908 | 0908.11 / 0908.12 / 0908.90 | Nutmeg, mace and cardamoms (whole or ground). |
| Seeds (anise, fennel, coriander, cumin, caraway, etc.) | 0909 | 0909.11 / 0909.21 / 0909.31 (varies by seed) | Seeds used as spices or for flavouring (anise, coriander, cumin, fennel, etc.). |
| Ginger, Saffron, Turmeric, Thyme, Bay, Curry blends & other spices | 0910 | 0910.10 / 0910.20 / 0910.99 (commodity-specific subheads) | Ginger, saffron, turmeric (curcuma), thyme, bay leaves, curry powders and other mixed spices. |
| Mixed spice blends (retail) | 0904 / 0910 | Depends on composition; often 0910.x or combined headings | Prepared spice mixtures — actual subheading depends on the main constituent and formulation. |
| Note: The HS headings above are 4-digit/6-digit level references; EU/TARIC uses more specific 8-digit codes. Always confirm the exact TARIC code with your customs broker/importer in Portugal and ensure the invoice/packing list use the precise 8-digit TARIC code for customs clearance. | |||
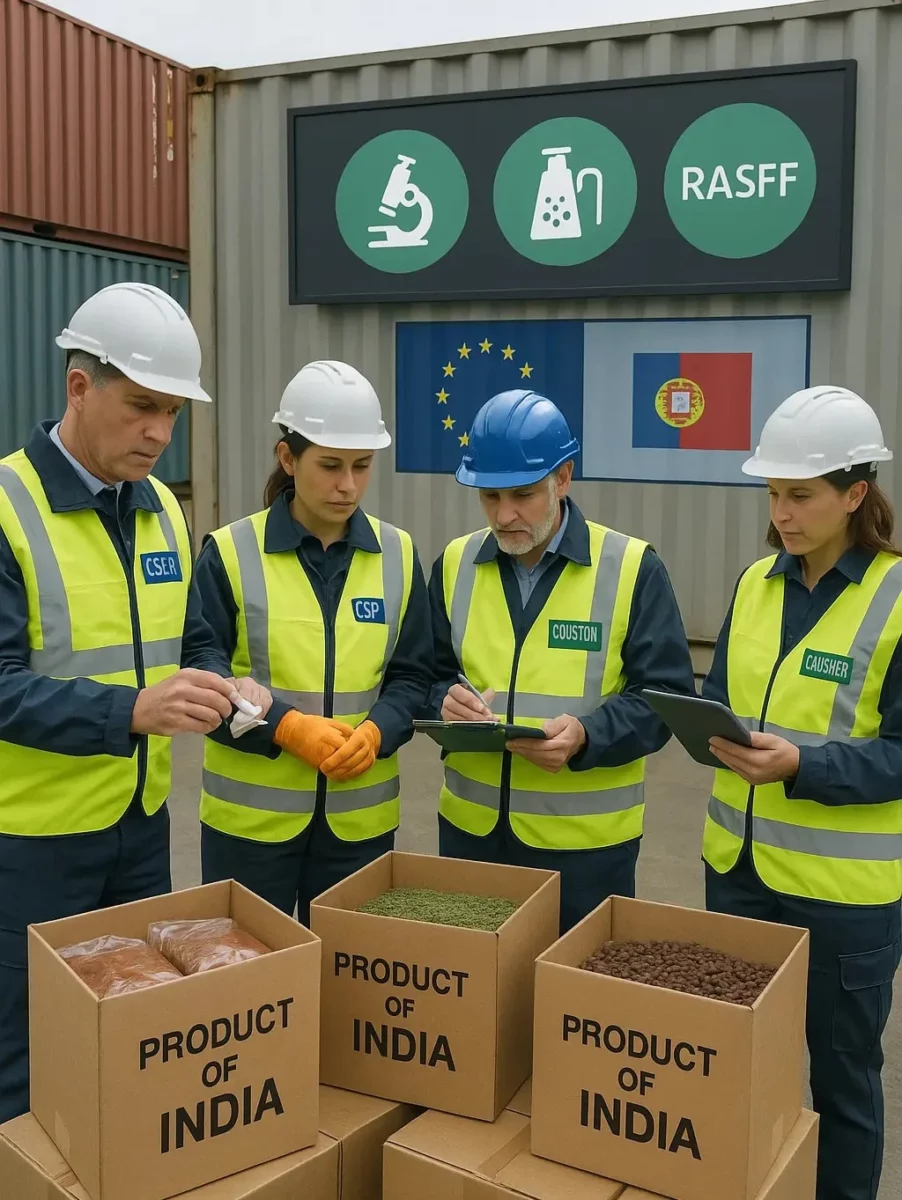
4. Border Controls and Official Checks
EU import regulations include official border controls to ensure safety:
- Contaminants & pesticide residues are tested.
- Packaging compliance is verified.
- Non-compliance can result in rejection, destruction, or return of the shipment.
- Significant issues are reported in the RASFF database, affecting future exports.

Please prepare complete test certificates, invoice, packing list, CoO, and make sure your Portuguese importer knows the process.

5. Product-Specific Guidelines
Spices
- Follow Reg. 2023/915 for aflatoxins, ochratoxin A, and heavy metals.
- Verify pesticide residues under Reg. 396/2005.
- Phytosanitary certificate only for fresh herbs or seeds for sowing.
- Label any allergens clearly under Reg. 1169/2011.
Tea
- Ensure pesticide MRLs and contaminants like pyrrolizidine alkaloids are within limits.
- Bulk tea for processing requires minimal labelling, but retail packaging must follow EU labelling rules.
- Provide lot numbers and batch traceability for consistency.
Coffee
- Check ochratoxin A and pesticide residues.
- Fumigation or pest-free certificates may be required for green beans.
- Use food-grade packaging and ensure proper sealing during transit.
6. Organic Exports — Opening Premium Markets
Organic exports require strict compliance with Regulation 2018/848:
- Every organic shipment must have a TRACES Certificate of Inspection (COI) before leaving India.
- The EU-recognised control body must issue the COI.
- Retail packaging should display the EU organic logo and control body code.
- TRACES COI ensures Portuguese customs allow your product to enter as certified organic.

Plan for extra lead time when shipping organic consignments, as TRACES certification and verification can take a few days.
7. Labelling and Consumer Information
EU Regulation 1169/2011 ensures consumers get complete information:
- Product name and ingredients
- Highlighted allergens
- Net quantity and lot number
- Country of origin (“Product of India”)
- Best-before or use-by date
- Storage instructions
- Nutritional information (mandatory for retail packs)
- Portuguese language labels for products sold in Portugal
Even for bulk shipments, your Portuguese buyer must be able to relabel or comply with EU regulations at the point of sale.
8. Private Standards & Buyer Expectations
European buyers increasingly demand traceability, sustainability, and safety guarantees:
- Residue and contaminant test certificates
- Fairtrade or Rainforest Alliance certification
- Organic certification with TRACES COI
- Batch consistency and robust traceability
Meeting these requirements helps differentiate your brand and reduces the risk of border rejections.
9. Commercial and Operational Tips
- Decide Incoterms (FOB, CIF, DAP) to clarify responsibility for shipping and insurance.
- Choose moisture-controlled containers for spices, tea, and coffee.
- Use pallets, shrink wrap, and sealed containers to prevent contamination or pest infestations.
- Communicate with your Portuguese importer and send pre-alert documents.
- Maintain traceability records for lot number, production date, and farm/origin details.
10. Long-Tail Search Topics Covered
Here are some long-tail queries relevant to exporters:
- “Phytosanitary certificate for spices to Portugal”
- “EU aflatoxin limits for turmeric and chilli 2025”
- “MRLs for tea leaves EU 2025”
- “TRACES COI for organic spices/coffee to Portugal”
We’ve covered these in context above, so your export process aligns with EU compliance.
11. Exporter’s Quick Checklist
- Lab testing: aflatoxins, ochratoxin A, heavy metals, pesticide residues
- Food-grade packaging compliant with Reg. 1935/2004
- Commercial Invoice, Packing List, Certificate of Origin
- Fumigation or pest-free statement (if required)
- Organic TRACES COI (if applicable)
- Correct HS/TARIC codes verified
- Label compliant with Reg. 1169/2011, in Portuguese for retail
- Pre-alert to Portuguese importer
- Traceability documents ready for inspection
Final Thoughts
Shipping Indian spices, tea, and coffee to Portugal can be profitable and sustainable, provided you follow:
- EU contaminants limits for spices (Reg. 2023/915)
- Pesticide MRLs for tea, coffee, and spices (Reg. 396/2005)
- Organic TRACES COI requirements (Reg. 2018/848)
- Labelling (Reg. 1169/2011) and packaging (Reg. 1935/2004)
With careful sourcing, proper testing, complete documentation, and smart logistics, your products won’t just reach Portugal they’ll stand out as safe, premium, and high-quality Indian exports.
FAQs
Only if shipping fresh herbs or seeds for sowing. Dried spices generally don’t require it.
Defined under Regulation 2023/915, aflatoxin and ochratoxin limits are strict. Pre-shipment testing is essential.
Under Regulation 396/2005, each pesticide used on tea leaves has a maximum residue level. Check updated lists before export.
It’s the mandatory Certificate of Inspection issued via TRACES under Regulation 2018/848. Without it, organic products cannot legally enter the EU.
Refer to the HS/TARIC table above. Using correct codes avoids customs delays and ensures compliance with EU import rules.