Did you know that your business can save thousands on international trade just by using a Certificate of Origin (COO)?
Whether you are exporting textiles, handicrafts, electronics, or food products, having the right paperwork can make a big difference in the tariffs and duties you pay.
But what exactly is a COO, and how does it help with tariff reduction? Let’s break it down step by step.
What is a Certificate of Origin
Imagine you are shipping your products overseas. Customs authorities want to know—where did these goods come from?
A Certificate of Origin (COO) answers that question by validating that your goods were processed or manufactured in a specific country.
Sounds normal, right? But it could be a game changer for exporters as this certificate can help unlock special tariff reductions and trade benefits under Free Trade Agreements (FTAs).
Types of Certificate of Origin
- Preferential Certificate of Origin- It confirms that goods qualify for reduced or zero tariffs because they come from countries that have trade agreements in place with the importing country.
- Non-Preferential Certificate of Origin- This certificate does not provide any special tariff benefit. Instead, it is used to support trade measures like anti-dumping duties, countervailing duties, or other regulatory requirements.
Certificate of Origin (COO) and Free Trade Agreements
You might be wondering—What do free trade agreements (FTAs) have to do with a Certificate of Origin?
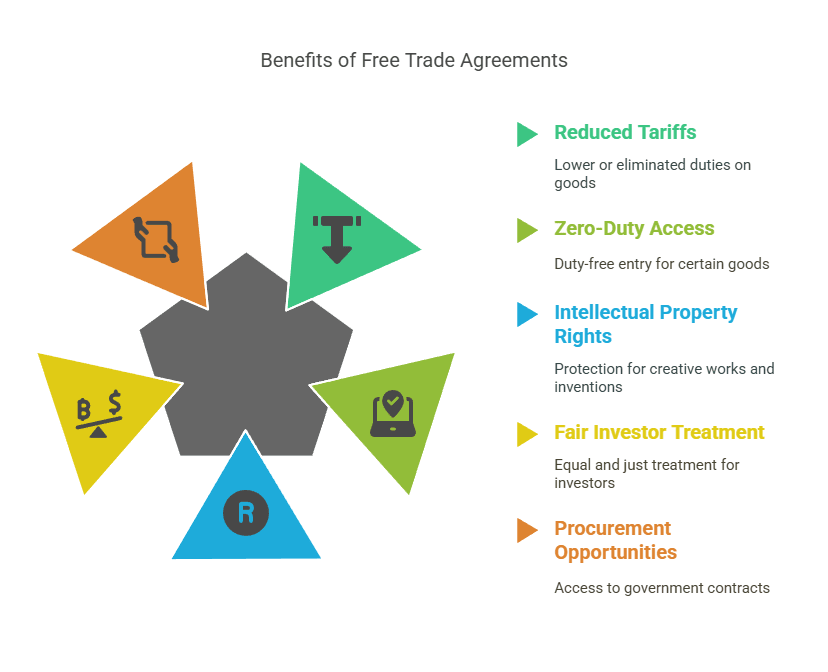
FTAs are agreements between countries that reduce or eliminate tariffs for certain goods. These agreements not only provide reduced or zero-duty access but also offer additional benefits such as:
- Stronger intellectual property rights protection.
- Fair treatment for domestic investors.
- Opportunities to participate in foreign government procurement processes.
But to benefit from these, exporters are required to prove that their products originate from the eligible country.
This is where a COO comes in handy. Some of the major FTAs that Indian businesses can benefit from include:
- India-Japan Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA)
- India-South Korea FTA
- India-UAE Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement
Let’s now talk about the United States. The U.S. has 14 free trade agreements (FTAs) with 20 countries, which makes around 40% of United States goods exports.
Table: US Free Trade Agreement Partner Countries
| Australia |
| Bahrain |
| Chile |
| CAFTA-DR (Costa Rica, Dominican Republic, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras and Nicaragua) |
| Colombia |
| Israel |
| Jordan |
| Korea |
| Morocco |
| Oman |
| Panama |
| Peru |
| Singapore |
| USMCA (United States-Canada-Mexico) (Formally NAFTA) |
Source: International Trade Administration, U.S. Department of Commerce
How Can a Certificate of Origin Reduce Tariffs
Picture this: You export handcrafted furniture from India to Europe. Without a COO, your products could face high tariffs at customs.
However, with a valid COO, your goods might qualify for reduced or even zero tariffs, making your products more competitive and profitable.
But the question is how?
A COO proves that your goods comply with trade agreements, helping importers benefit from lower duty rates under agreements like India-ASEAN Free Trade Agreement, India-EU Trade Agreement, South Asian Free Trade Area (SAFTA), and others.
By submitting a valid COO, you can enjoy lower import duties, duty-free exports (if applicable under specific trade agreements), and smoother customs clearance.
Who Fills Out the FTA Certificate of Origin
FTA certificates or declarations are usually completed by an individual who is well-versed in the transaction details—most commonly, the exporter. However, in some cases, the exporter may not necessarily be the producer of the goods. Since the producer possesses the most detailed knowledge of the product’s compliance with rules of origin (ROO), they may be requested to provide the FTA certificate, even if they are not directly involved in the export process.
Who Claims the FTA Preference
It is the responsibility of the importer or buyer to claim the FTA preference when clearing customs in the importing country. However, the importer relies on the information provided by the exporter in the certificate or declaration to validate the claim. This documentation may be required to demonstrate eligibility for tariff reductions or exemptions to the customs authorities in the destination country.
Tools and Resources for Exporters
Exporting can feel overwhelming, but the right tools can simplify the process. Whether you are looking for information on tariffs, trade agreements, or classification codes, these resources can help:
Rules of Origin Facilitator
This online tool, developed by the International Trade Centre (ITC), offers easy access to a global database of rules of origin and trade agreements.
The Rules of Origin Facilitator has been designed primarily for small and medium enterprises (SMEs). It provides quick access to information on applicable import duties, available duty exemptions, origin criteria, and certification processes.
Harmonized System (HS) Codes
The HS code is an internationally recognized system for classifying products in global trade.
Knowing the correct HS code for your product is essential to determine the applicable tariffs and comply with customs regulations.
Tools for U.S. Exporters
FTA Tariff Tool- This platform allows U.S. exporters to check the tariff rates imposed by partner countries under free trade agreements (FTAs). Exporters can find out current duty rates and determine when tariffs will be reduced or eliminated.
Customs Info Database- A comprehensive resource offering free access to tariff data for U.S. exporters looking to ship to multiple countries. A tutorial video is also available to guide exporters through the registration process and usage of the database.
Tools for Indian Exporters
Indian Trade Portal- Provides information on tariff concessions, trade agreements, and Rules of Origin applicable to Indian exporters.
Indian Customs Tariff and Trade Tools- Head to platforms like the Indian Customs Tariff Database or the DGFT’s website to know tariff rates and information related to India’s FTAs.
Preferential Trade Agreements (PTA) Finder- Tools like the India-ASEAN Trade in Goods Agreement Tariff Calculator or regional trade agreement-specific platforms can help you understand tariffs and Rules of Origin for your products.
Export Promotion Councils (EPCs)- You can also consult Export Promotion Councils for guidance on leveraging FTAs and determining applicable tariff rates.
Why Should You Bother with a COO
Thinking if it is really worth the effort to apply for COO? The answer is YES.
Here’s why:
- Save Money with Customs Duty Waivers
Many countries offer tariff concessions if you can prove your product’s origin. Without a COO, you could end up paying full import duties. - Expand to New Markets
With reduced tariffs, your products become more attractive to international buyers. More sales, more profits! - Boost Your Credibility
A COO reassures your customers and partners that they’re getting genuine products from your country, enhancing trust and business relationships.
Make sure to submit the COO while exporting to countries with FTA agreements. This can improve profitability and create new market opportunities by eliminating trade barriers and reducing tariffs. If your product qualifies for FTA benefits, leveraging these agreements can be a strategic move to enhance competitiveness.
Common Challenges in Using a COO
Applying for a COO may seem straightforward, but businesses often face some hurdles:
- Confusing Trade Agreements
Different FTAs have different requirements, knowing which one applies to your goods or products can be tricky. - Documentation Errors
Even minor mistakes in product descriptions or HS codes can lead to customs issues. - Administrative Delays
Applying for COOs manually can take time; using online platforms can speed up the process.
Research on how to obtain a Certificate of Origin and learn about the documents that are mandatory to obtain it to avoid last-minute delays.
Tip: Always double check the accuracy of your documentation before submission.
Conclusion
By now, you must have understood how a Certificate of Origin and tariffs go hand in hand. Whether you are exporting clothing, machinery, or food products, a COO can help you qualify for duty-free exports, save you money through customs duty waivers, and help you strengthen your position in global markets.
Taking advantage of Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) can help businesses stay competitive by reducing or eliminating duties on eligible products. While an FTA certificate of origin is not mandatory to clear customs, goods shipped without it may face standard tariff rates. By including the Certificate of Origin, exporters can unlock significant cost savings and remain competitive in global markets.
Happy Shipping!
FAQs
A Certificate of Origin is an official document that certifies where a product was manufactured or processed. It helps customs authorities verify the origin of products for tariff and duty purposes.
Yes, a valid COO allows you to qualify for reduced or zero tariffs under Free Trade Agreements (FTAs). This helps make your products more competitive in global markets.
While not always mandatory, a COO is crucial to access trade benefits under FTAs and to avoid paying standard tariff rates. It is primarily required for preferential trade benefits or when requested by the importer.
FTAs provide exporters with tariff reductions, duty-free access, stronger intellectual property protection, and improved opportunities to compete in foreign markets, provided they submit valid documents.
The exporter, who is knowledgeable about the transaction, typically fills out the FTA certificate. However, in some cases, the producer may be required to provide the necessary documentation.
The importer or buyer claims the FTA preference at customs using the COO provided by the exporter to qualify for reduced duties.
Without a COO, your goods may face higher tariffs and could be subjected to delays or additional scrutiny by customs authorities.