AI Summary
India’s export sector is growing steadily, fueled by strong sectors and expanding e-commerce participation, creating new global opportunities for businesses. Despite challenges like trade gaps, currency shifts, and logistics costs, exporters who explore new markets, stay compliant, and leverage digital platforms can scale globally and strengthen India’s trade position.
Exports play a crucial role in a country’s economy, driving growth, creating jobs, and strengthening international trade relationships. India has been making significant progress in its export sector, with an impressive hike in merchandise and service exports. This rise is not just a statistic; it has a direct impact on businesses, employment opportunities, and the global perception of India as a key trading nation.
With increasing globalisation and digital transformation, the world is more connected than ever, making it an ideal time for Indian businesses to scale their exports. Strengthening the export sector enhances the country’s economic resilience, increases foreign exchange reserves, and reduces trade deficits. The more businesses engage in exports, the more India cements its position as a global trade powerhouse.

International e-commerce shipping is also becoming an essential part of this growth, as more businesses leverage e-commerce platforms to sell globally. E-commerce exports from India are seeing a rapid rise, helping businesses tap into newer markets and expand their reach beyond traditional trading methods.
In this blog, we will break down the latest export trends in India, key insights, and their implications for businesses and the economy. Whether you’re a business owner looking to expand globally or curious about international trade, this blog will help you understand India’s export landscape in the simplest terms and inspire action toward leveraging global opportunities.
India’s Trade Performance — December 2025 (Updated)
🌐 Trade Snapshot (Merchandise + Services)
| Category | Amount | YoY Change |
|---|---|---|
| Total Exports | USD 68.27 billion | +4.52% |
| Total Imports | USD 79.99 billion | +6.07% |
| Trade Deficit | USD −11.72 billion | ↑ from −10.10 billion |
📦 Merchandise Trade (July 2025)
| Exports | Imports | Deficit |
|---|---|---|
| USD 37.24 billion (+7.3%) | USD 64.59 billion (+8.6%) | USD −27.35 billion |
🚀 Select Export Categories (July 2025)
| Category | Value | Change |
|---|---|---|
| Electronics | USD 3.77 billion | +33.9% |
| Engineering Goods | USD 10.43 billion | +13.8% |
| Gems & Jewellery | USD 2.39 billion | +28.9% |
| Drugs & Pharmaceuticals | USD 2.66 billion | +14.1% |
| Organic & Inorganic Chemicals | USD 2.47 billion | +7.2% |
🔍 Non-Petroleum & Non-Gems Exports (July 2025)
- Exports: USD 30.51 billion (+12.7%)
- Imports: USD 42.79 billion (from USD 40.04 billion)
📊 Cumulative Trade (April–July 2025)
- Total Exports: USD 277.63 billion (+5.23%)
- Total Imports: USD 308.91 billion (+4.25%)
- Combined Deficit: USD −31.28 billion (vs −32.48 billion)
- Merchandise Exports: USD 149.20 billion (+3.07%)
- Merchandise Imports: USD 244.01 billion (+5.30%)
- Non-Petroleum Exports: USD 127.46 billion (+7.70%)
Insights for Exporters
Export growth is steady, but imports are rising faster, widening the trade gap. Strong performance in electronics, engineering goods, pharmaceuticals, and jewellery shows shifting export dynamics. Services exports remain resilient and help balance the deficit. Exporters should closely watch global trade policies, especially U.S. tariff actions, which may affect competitiveness.
| Region | Export Value (USD) | Top Commodities | Notable Trade Trends |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States 🇺🇸 | $79.44 Billion (2024) |
– Gems, Precious Metals – Electronics, Pharma, Machinery – Apparel, Vehicles |
iPhone exports up 76%; US–India trade deal talks ongoing; Diamond exports impacted by tariffs |
| European Union 🇪🇺 | $52.34 Billion (2024) |
– Textiles & Apparel – Machinery & Mechanical Items – Agricultural Products |
Highest trade levels in a decade; Ongoing FTA dialogues to improve access |
| Middle East (UAE) | $37.1 Billion (2024) |
– Gems & Jewelry – Agricultural Produce (Mangoes) – Mineral Fuels |
Chausa & Dussehri mango exports rising; Strong bilateral trade with UAE |
| Africa | $45 Billion (2024) |
– Mineral Fuels – Pharmaceuticals – Food & Engineering Goods |
Heavy-haul locomotives exported to Guinea; Growing engineering exports |
| ASEAN | $44 Billion (FY 2023) |
– Engineering Goods – Agriculture Products – Chemicals |
India–ASEAN FTA being renegotiated; Push to resolve trade imbalances |
What’s Driving This Growth
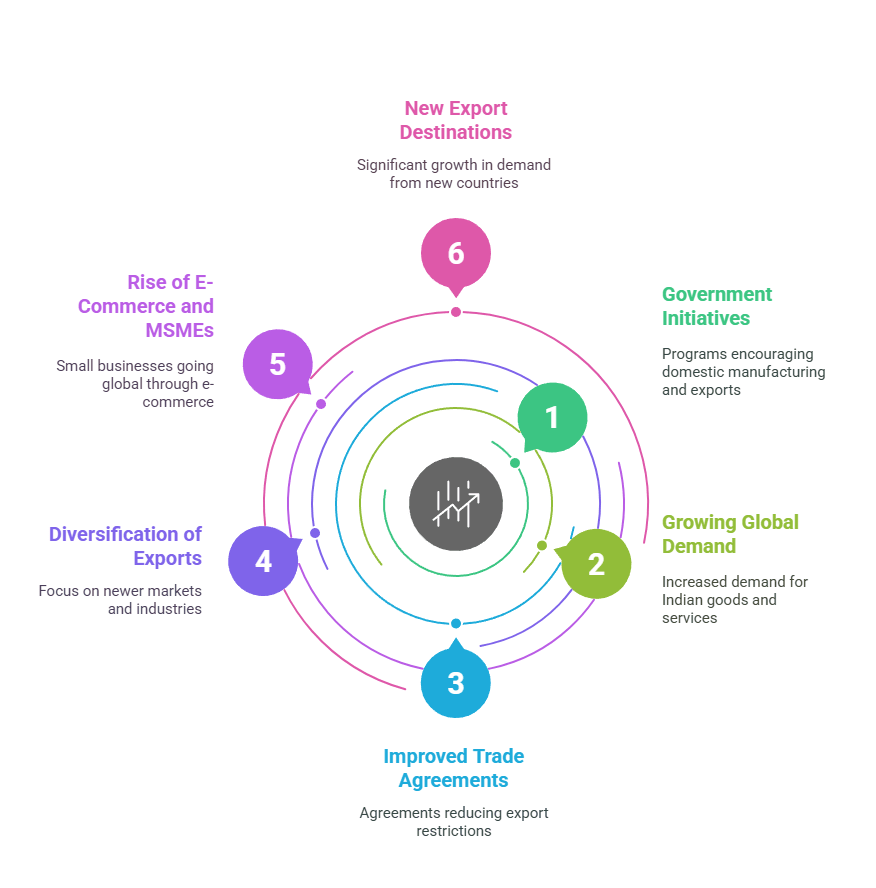
Several factors are contributing to India’s export growth:
- Government Initiatives: Programs like ‘Make in India’ and ‘Production-Linked Incentive (PLI)’ are encouraging domestic manufacturing and exports.
- Growing Global Demand: As economies recover post-pandemic, demand for Indian goods and services is increasing.
- Improved Trade Agreements: India has been entering trade agreements with key partners, reducing export restrictions.
- Diversification of Exports: Indian exporters are shifting focus to newer markets and industries beyond traditional sectors.
- Rise of E-Commerce and MSMEs: More small and medium businesses are going global, leveraging platforms like Amazon, Etsy, and Shopify.
- New Export Destinations: Countries like the USA, Japan, Bangladesh, the UK, and Nepal have shown significant growth in demand for Indian products.
- Strategic Push for India Export Growth: Export facilitation through digital platforms, simplified documentation, and logistics support is accelerating India’s position as a reliable trade partner.
Challenges in Exporting from India
India continues to post strong export numbers, but exporters are navigating several critical challenges in 2025:
- Global Policy Uncertainty and Trade Tensions
Export competitiveness is under threat due to steep U.S. tariffs—currently at 50% on many product; targeting textiles, gems, footwear, and more. These retaliatory tariffs are adding cost pressure and disrupting market access. - Rapid Currency Depreciation
The Indian rupee has weakened to nearly ₹88 to the U.S. dollar—its lowest level ever. This devaluation erodes exporter margins and increases the real cost of imported inputs, while also raising inflation risks. - Competitive Pressure from Rising Imports
India’s trade deficit with China has ballooned to approximately USD 99 billion, with imports exceeding USD 113 billion in FY 24–25, while exports to China fell below USD 15 billion. This imbalance highlights low-value export growth and heavy reliance on Chinese inputs. - Logistics & Supply Chain Bottlenecks
Despite government initiatives (such as Multi-Modal Logistics Parks), India’s freight structure remains costly; around 13% of goods value versus 8–10% in peer economies. High costs, port congestion, infrastructure gaps, and slow cargo movement continue to hinder exporters. - Regulatory Complexity & Compliance Hurdles
Exporters face layers of documentation, certifications, and shifting standards across destination markets. Recent U.S. policy changes demand immediate financial and operational adjustments, especially for smaller firms. - Currency Fluctuation and Capital Outflows
The rupee’s volatility, combined with capital flight (over USD 2.4 billion in equity outflows recently) makes financial management tough. This undermines predictability in export planning and investment.
For more in-depth information, refer: https://www.commerce.gov.in/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/PIB-Release-January-2025-fin.pdf
Opportunities for Exporters
If you’re an exporter or planning to start, here’s how you can take advantage of this growth:
- Explore New Markets: Don’t just focus on the US and Europe. Emerging markets in Africa, the Middle East, and Southeast Asia are seeing rising demand.
- Leverage Digital Platforms: Selling on global e-commerce platforms can help you reach more buyers.
- Stay Compliant: Understand and follow international trade regulations to avoid penalties.
- Use Efficient Shipping Solutions: Partner with reliable logistics providers to ensure timely delivery.
- Focus on Quality: Competing in international markets requires high-quality standards and certifications.
Conclusion
India’s export sector is on a strong upward trajectory, driven by supportive policies, increasing global demand, and emerging market opportunities. Despite challenges, businesses that adapt to new trends and invest in quality and efficiency will benefit the most. Whether you are an established exporter or a new player, understanding these trends will help you make informed decisions and grow successfully in the global market.
With the Indian government actively targeting higher export volumes and enhancing trade infrastructure, there has never been a better time for businesses to explore global opportunities. International e-commerce shipping and e-commerce export from India are critical in achieving these goals. Exporting is not just for large corporations—small and medium businesses can also benefit immensely.
The push for exports will strengthen India’s position in the global economy, create more jobs, and drive innovation across industries. If you are in business, consider expanding internationally and becoming a part of India’s growing export success story.
Frequently Asked Questions
Exports drive economic growth, create jobs, increase foreign exchange reserves, and strengthen India’s position in global trade.
India’s total exports, including both merchandise and services, reached USD 824.9 billion in 2024–25, recording a growth of around 6 per cent compared to the previous year. During April–January 2024–25, exports stood at USD 682.59 billion, which was a 7.21 per cent increase over the same period in 2023–24.
The strongest contributions came from electronics, pharmaceuticals, engineering goods, rice, and gems and jewellery. Electronics exports jumped by nearly 79 per cent, pharmaceuticals by over 21 per cent, rice by about 45 per cent, engineering goods by more than 7 per cent, and gems and jewellery by roughly 16 per cent. Services exports also rose sharply to about USD 388 billion, providing additional momentum to India’s overall export growth.
E-commerce enables Indian businesses to reach global markets, simplifying international trade and expanding beyond traditional export methods.
Businesses can scale operations, increase revenue, expand their global presence, and reduce dependence on domestic demand, making them more competitive internationally.