Exporting from India to the European Union (EU) can unlock incredible growth opportunities for businesses, but navigating the regulatory landscape requires careful planning and thorough documentation. Here’s your ultimate guide to ensure a seamless export journey:
Essential Steps for Exporting
- Obtain an Import Export Code (IEC): An IEC, issued by the Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT), is a compulsory 10-digit identifier required for international trade activities.
- Enrol with Export Promotion Councils (EPCs): Joining an EPC related to your product category can provide support such as market insights, financial incentives, and networking opportunities.
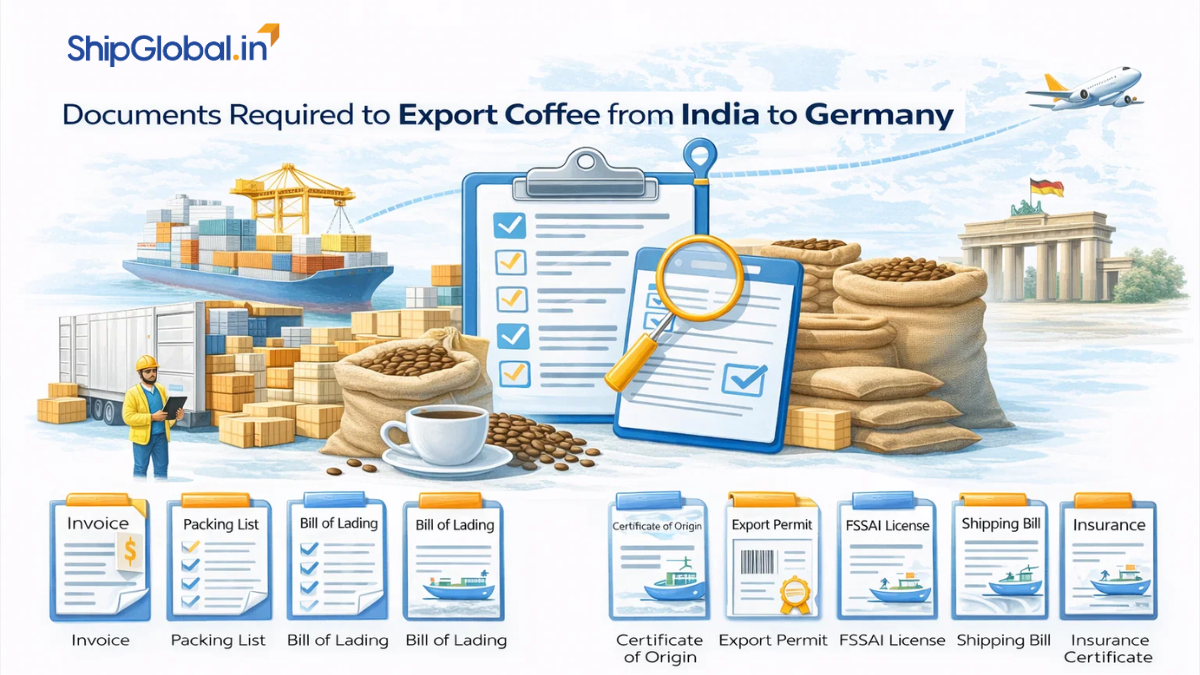
- Prepare Key Export Documents: Ensure the accuracy of critical paperwork including:
- Commercial Invoice: A comprehensive document that provides essential details of the transaction, such as the description of goods, quantity, unit price, total value, terms of sale (FOB, CIF), and the transaction currency. It serves as the primary document for customs valuation and taxation
- Packing List: Offers a detailed breakdown of the shipment, specifying the contents of each package, weight, dimensions, and any special handling instructions. It helps customs authorities verify the shipment’s contents against the invoice.
- Bill of Lading (B/L) or Airway Bill (AWB): The B/L applies to sea shipments, while AWB is used for air shipments. These documents act as a receipt for goods, proof of shipment, and a document of title that can be transferred to claim ownership.
- Certificate of Origin: Officially certifies the country where the goods were manufactured. This document is crucial for claiming tariff benefits under trade agreements between India and the EU.
- Export License: required for the export of restricted items such as pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and defence equipment. Exporters should verify if their products need such licensing.
- Phytosanitary Certificate: Necessary for the export of plant-based products, verifying that the goods meet EU safety and quality standards and are free from pests and diseases.
- Health Certificate: Ensures that food and beverage products comply with EU health and hygiene regulations, verifying that they are safe for consumption.
- Obtain Customs Clearance: Submit the shipping bill, pay applicable duties, and secure clearance from customs authorities to avoid delays.
- Ship Your Goods: Coordinate transportation while complying with all regulatory and safety requirements throughout the process.

Comprehending EU Import Regulations
To comply with EU import rules, exporters should understand the Union Customs Code (UCC) and specific product regulations, such as:
- Customs Valuation of Tariff Codes: Properly classifying products using Harmonised System (HS) codes ensures accurate duty calculation.
- Product Compliance Standards: Products may require CE Marking, REACH compliance, or food safety certifications based on type.
- Preferential Tariffs: India’s trade agreements with the EU offer reduced tariffs for goods meeting origin criteria.
Essential Import Documents for the EU
Essential EU Import Documentation
Importing goods into the European Union (EU) requires proper documentation to ensure smooth customs clearance and regulatory compliance. Accurate paperwork helps avoid delays, ensures correct duty payments, and maintains trade efficiency.
- Single Administrative Document (SAD): The SAD is the primary customs declaration, including shipment details like product description, customs value, origin, destination, and duties.
- Import Licence: Required for restricted items such as agricultural goods, chemicals, or dual-use products. Issued by the appropriate EU authority.
- Technical Documentation: Verifies compliance with EU standards and may include specifications, Safety Data Sheets (SDS), test reports, and certificates of conformity.
- Proof of Origin: Confirms the origin of goods and impacts tariff rates. This could be a certificate of origin or a self-declaration by the exporter.
Ensuring proper documentation simplifies the import process, prevents legal issues, and supports strong business relationships in the EU market.
Tariffs and Taxes
Exporting to the EU involves understanding the tariffs and taxes that may be applied to your goods, as these financial factors can directly influence your profit margins. Accurate cost estimation ensures better pricing strategies and profitability.
Exports Tariffs in India for businesses and individuals engaged in international trade, understanding India’s exports tariffs (also known as export duties) is essential. These tariffs serve multiple strategic purposes and can impact trade decisions significantly.
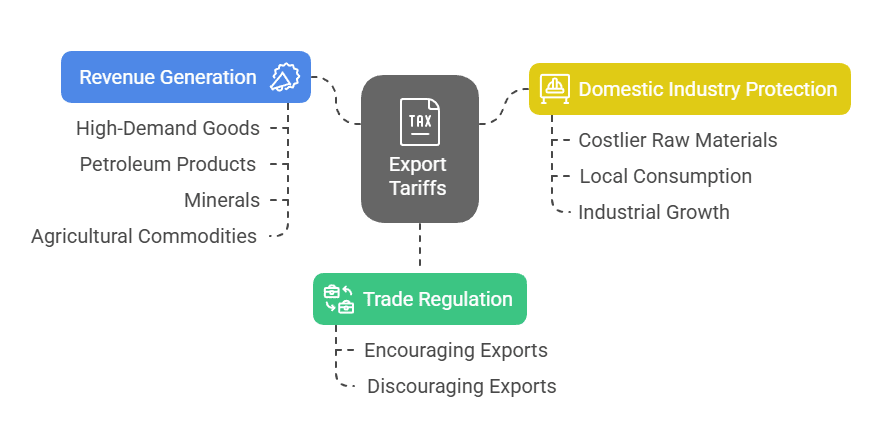
Key Objectives of Export Tariffs
- Trade Regulation: Export Tariffs control the movement of goods by either encouraging or discouraging the export of certain products. For example, high tariffs on raw materials like iron ore and select agricultural items help retain essential resources for domestic use
- Revenue Generation: Export duties also contribute to national revenue particularly on high-demand goods such as petroleum products, minerals and agricultural commodities.
- Domestic Industry Protection: By making the export of raw materials costlier, tariffs can safeguard domestic injuries from foreign competition. This approach encourages local consumption and production, boosting employment and industrial growth.
Specific Rates and Types of Export Tariffs
Export Duties in India: Key Insights
Export duties in India differ based on the product and prevailing economic policies. These duties are often used to promote domestic value addition and regulate the supply of key resources.
- Mica Exports: Export duties have historically been imposed on mica to encourage value-added processing within India.
- Leather Goods: Export duties may apply to raw hides and skins, promoting the domestic manufacturing of finished leather products.
Official Resources for Export Tariffs
Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC): The CBIC website provides the latest tariff rates and regulatory updates
Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT): The DGFT portal issues notifications on tariff changes and export policies.
Indian Customs Tariff Schedule: This detailed document outlines applicable export duties for various products and categories.
Import duties and taxes in the EU when exporting to the EU, It’s essential to understand the duties and taxes applied to imported goods, as they can affect pricing and market entry strategies.
Key Components of Import Duties and Taxes
Common External Tariff (CET):
Product Classification: Goods are classified under the Harmonised system (HS) code, determining the tariff rate. Accurate classification helps avoid underpayment or overpayment of duties
Country of Origin: Goods originating from countries with preferential trade agreements, such as the EU-India trade pact, may benefit from reduced or zero tariffs if origin criteria are met.
Value Added Tax (VAT)
VAT is a consumption tax applied at each stage of the supply chain and collected from the end consumer.
VAT rates in EU countries generally range from 15% to 27% with lower rates for essential goods like pharmaceuticals and educational materials.
Excise Duties
Excise duties are levied on specific products such alcoholic beverages, tobacco and fuel. These duties vary by product and country. For example, spirits imported into Germany may face higher excise duties in Spain than in Germany due to national policies.
Conclusion
By staying well-informed about the various tariffs and tax structures applicable in both the exporting and importing regions, exporters can develop more effective pricing strategies that align with market demands and regulatory requirements.
This proactive approach not only helps in accurately forecasting overall costs but also minimises financial risks associated with unexpected charges or compliance issues. As a result, businesses can better position themselves for long term success, build stronger trade relationships, and take advantage of growth opportunities in the competitive EU market.
FAQs for Export Rules and Documents: India to Europe
The Import Export Code (IEC) is a mandatory 10-digit identifier issued by the Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT) required for conducting international trade.
The SAD is the primary customs declaration for the EU, detailing shipment information like product description, origin, and duties.
Enrolling with EPCs provides market insights, financial incentives, and networking opportunities tailored to your product category.
No. Most goods fall under the “free” category, which means no special license is required. However, restricted goods (like defense items, pharmaceuticals, chemicals) need DGFT-issued export licenses.
No, Exports from India are zero-rated under GST, and no VAT is payable in Europe at the export stage. However, the importer in Europe may be liable to pay VAT upon import clearance.