If you’re moving goods across India under GST, chances are you’ve heard of the e Way Bill. It’s one of those compliance steps that often seems complex at first glance, but once you get the hang of it, it’s actually pretty straightforward. Let’s break it down together in a simple, way.
What is an E-Way Bill
The eWay Bill (short for Electronic Way Bill) is basically a digital paper trail for goods on the move. It is generated electronically on the GST portal. This document is required for the movement of goods worth more than INR 50,000, either within a state or across state borders. It’s meant to track the flow of goods and reduce tax evasion. Think of it like a boarding pass for your cargo – if it’s going somewhere, there better be a bill to show for it!
The E-Way Bill system ensures that goods are transported in compliance with GST laws. Under Rule 138 of the CGST Rules, 2017, every registered person who causes movement of goods of consignment value exceeding INR 50,000 is required to generate an E-Way Bill.
Why Do We Need an E-Way Bill
Before GST, each state had its own way of tracking goods, octroi, entry tax, permits, you name it. It created bottlenecks at checkpoints and a whole lot of paperwork. The E-Way Bill system fixes that by creating a single, nationwide electronic system to monitor goods in transit.
Here’s what it helps with:
- Prevents tax leakage.
- Reduces waiting times at state borders.
- Simplifies compliance for businesses.
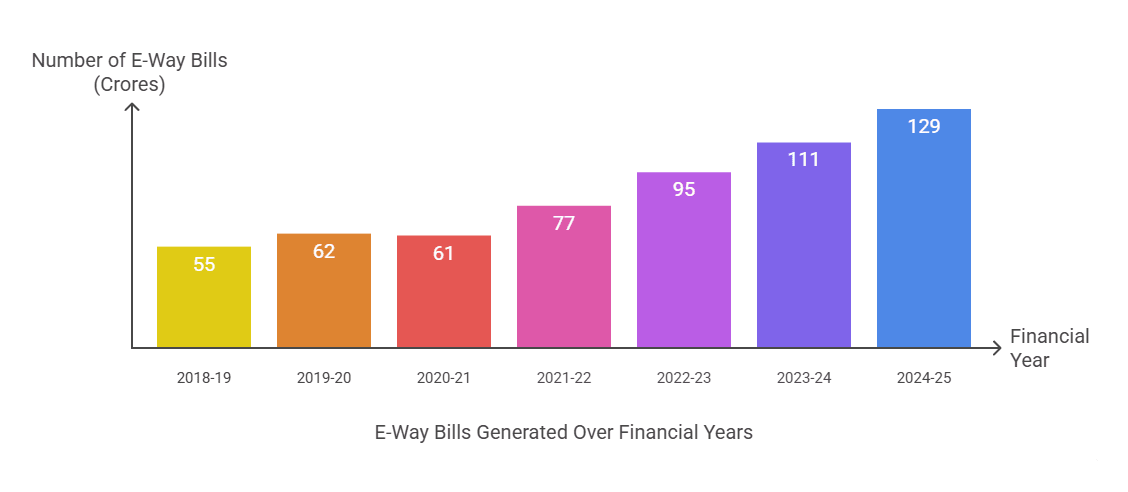
- Enables real time tracking of goods.
So, in short, it’s cleaner, quicker, and smarter.
Key Components of an EWay Bill System
The E-Way Bill consists of two main parts:
Part A: Part A primarily captures the transaction details. This includes:
- GSTIN of the recipient
- Place of delivery (PIN code)
- Invoice or challan number and date
- Value of goods
- HSN code
- Reason for transportation (e.g., supply, job work, return)
- Transport document number (LR number, railway receipt, airway bill, etc.)
Part B: This part contains transportation details such as:
- Vehicle number
- Transporter ID
So, Part A is crucial for defining what is being transported and why, whereas Part B helps track how it is being transported.
When is the E-Way Bill Mandatory
You’ll need to generate an E-Way Bill in any of the following conditions:
- Movement of goods worth more than ₹50,000: If you’re moving goods worth more than ₹50,000 in value (whether for supply, return, job work, or transfer to another branch).
- Interstate and intrastate transportation: If the movement is interstate (from one state to another) or even within a state, depending on local rules.
- Import and export related movement.
- Transportation for job work purposes.
Who Should Generate an E-Way Bill
Now, who’s responsible for generating the bill? It depends on who’s causing the movement:
- Registered Supplier/Consignor: If you’re sending goods using your own vehicle, a hired vehicle, or by rail, air, or ship.
- Transporter: If you’ve handed over goods to a transporter and neither you (the supplier) nor the recipient have generated the E-Way Bill.
- Recipient: If the goods are being sent to you and you’re registered under GST, you might also need to step in if no one else has generated the bill.
So, the rule of thumb is—whoever is causing the movement should generate the bill.
How to Generate the Bill
There are several methods to generate an E-Way Bill:
| Method | Details |
|---|---|
| GST E-Way Bill Portal | Access the portal at ewaybillgst.gov.in |
| SMS-based Facility | Suitable for small businesses and transporters |
| Android App | Enables on-the-go access for users |
| Bulk Upload Tools | Useful for businesses handling multiple invoices |
| API Integration | Designed for businesses integrating with ERP software |
Steps to Generate the Bill:
- Log in to the E-Way Bill Portal.
- Navigate to ‘Generate New’ and fill in Part A and Part B details.
- Submit the form, and voila – you’ll get a unique E-Way Bill Number (EBN).
- Share the EBN with the transporter and recipient; carry the E-Way Bill copy physically or electronically for smooth operations
Benefits of E Way Bill
| Benefit Area | Description |
|---|---|
| Simplifies Goods Movement | Pan-India uniformity and a single e-Way Bill for the entire journey across states. |
| Reduces Documentation and Physical Barriers | Eliminates check posts and reduces paperwork with digital e-Way Bill system. |
| Faster Transit Time | Minimizes delays at borders and speeds up deliveries through automated verifications. |
| Enhances Transparency and Tracking | Enables real-time tracking and creates a digital audit trail of goods movement. |
| Reduces Tax Evasion | Improves compliance and prevents underreporting with GST return integration. |
| Promotes Ease of Doing Business | API integration with ERPs and aligns with Digital India initiatives for smooth operations. |
| Data Insights for Business | Provides shipment analytics for planning, forecasting, and vendor management. |
| Better Enforcement & Reduced Malpractice | Minimizes fake invoicing and enables smart inspections with digital records. |
Consignor Vs Consignee Responsibilities in E-Way Bill System Compliance
When it comes to transporting goods in India under GST, the E-Way Bill isn’t just a formality – it’s your cargo’s digital passport. Whether you’re the consignor sending out goods or the consignee receiving them, both sides of the transaction have specific duties that must be followed to stay on the right side of the law.
Let’s break down what each party is responsible for, in a way that actually makes sense (and helps avoid penalties and headaches later).
What the Consignor Needs To Do
Here’s your to-do list:
- Kickstart The E-Way Bill: If you’re arranging transport (your own vehicle, a hired one, or even shipping by air or rail), you’re the one who needs to generate the e-way bill before the goods hit the road.
- Enter Key Details: You’ll need to fill in Part A (about the goods, invoice, HSN code, GSTINs, etc.) and ensure Part B (vehicle number or transporter ID) is completed.
- Hand Over The Goods + Paperwork: Don’t forget to give your transporter both the invoice and either a physical or digital copy of the e-way bill.
- Stay Organized: Keep a copy of the e-way bill handy for audits or compliance checks—yes, even if everything went smoothly.
What the Consignee Needs To Do
Here’s how to stay compliant:
- Double-Check The Shipment: Once goods arrive, check that what you received matches the e-way bill and invoice. Any mismatch? That’s a red flag.
- Generating Your Own E-Way Bill: If you’re arranging pickup (say, you’re collecting goods from the supplier’s warehouse), then it’s your duty to create the e-way bill.
- Verify Before You Accept: Make sure the goods are riding along with a valid e-way bill. No one wants a surprise inspection and fine.
- File It Away: Just like the consignor, you should save a copy of every e-way bill linked to your purchases.
| Task | Consignor (Sender) | Consignee (Receiver) |
|---|---|---|
| Starts the shipment | Yes | Sometimes (if arranging pickup) |
| Generates e-way bill | Yes, if using own/hired transport | Yes, if arranging transportation |
| Fills Part A | Yes | Only if generating the bill |
| Fills Part B (Vehicle Info) | Yes (or assigns to transporter) | Yes, if they’re the one dispatching vehicle |
| Provides docs to transporter | Yes – invoice + e-way bill | Not required |
| Retains e-way bill records | Yes | Yes |
| Verifies goods on receipt | Not needed | Absolutely |
Getting this wrong can cost you. Under Section 129 of the CGST Act, authorities can detain your goods, confiscate the truck, and slap heavy penalties for incorrect or missing e-way bills.
But when both consignor and consignee play their part, goods move without friction, compliance is seamless, and everyone wins.
What are Consolidated eWay Bills
When a transporter needs to move multiple consignments in a single vehicle, managing individual e-Way Bills can be cumbersome. A consolidated e-Way Bill simplifies this by bundling multiple e-Way Bills into one document.
Features of Consolidated Bills
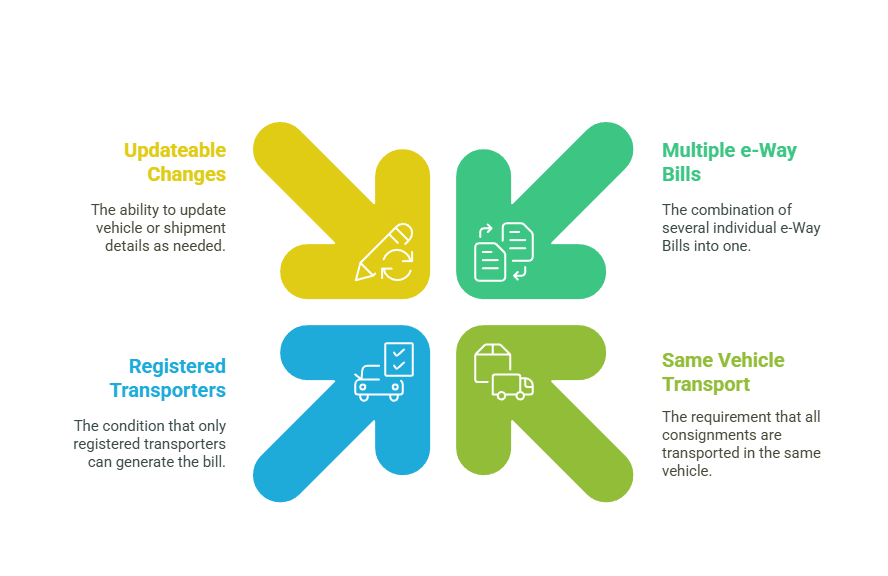
- Combines multiple e-Way Bills.
- Applicable only if the consignments are transported in the same vehicle.
- Only registered transporters can generate a consolidated e-Way Bill.
- Changes in vehicle or shipment can be updated.
When is a Consolidated Bill Needed
- Multiple e-Way Bills for different consignments are to be moved together.
- Same transporter handling different customers’ goods in one trip.
- Facilitates easy checking by authorities during transit.
Steps to Generate It
- Log into the e-Way Bill portal.
- Select “Generate Consolidated e-Way Bill”.
- Enter the e-Way Bill numbers for each consignment.
- Fill in common transport details (vehicle number, etc.).
- Generate and carry a copy during transportation.
Advantages of Consolidated Bills
- Reduces documentation workload.
- Easy for transporters to manage multiple consignments.
- Faster transit through check posts.
- Enhances operational efficiency.
Important Points to Note
- Only active and valid e-Way Bills can be consolidated.
- If any e-Way Bill included expires, update or remove it.
- Update vehicle details if vehicle changes mid-transit.
Validity of eWay Bills
These documents don’t last forever – they have a shelf life based on distance:
- Up to 200 km: 1 day.
- For every additional 200 km: Additional 1 day.
If the journey cannot be completed within the validity period, the e-Way Bill must be extended before expiry.
When is E-Way Bill Not Required
An E-Way Bill is generally not required in the following situations:
- Consignment Value ≤ ₹50,000:
No e-Way Bill is needed if the total value of goods transported (including tax) is ₹50,000 or less, except for specific cases like interstate movement of certain goods.
- Non-Motorized Conveyance:
If goods are transported using non-motorized vehicles (e.g., hand carts, animal-driven carts), no e-Way Bill is required.
- Exempted Goods:
If goods being transported are fully exempt from GST, no e-Way Bill is needed. Examples include live animals, fresh fruits, vegetables, and unprocessed milk.
- Customs Movement:
Movement of goods under customs supervision (e.g., bonded warehouse to port, port to ICD) is exempt.
- Government and Defense Supplies:
Transport of goods by Ministry of Defence is exempt.
- Empty Cargo Containers:
No E-Way Bill is required for movement of empty containers.
- Movement Within 10 km (Intrastate):
In some states, if the distance between the consignor and the transporter is less than 10 km, Part B (vehicle details) is not required—though this may vary by state.
Bill Cancellation
Sometimes, mistakes happen during e-Way Bill generation, or shipments are canceled. In such cases, cancelling an e-Way Bill is essential to avoid penalties and maintain correct records.
Reasons to Cancel
- Goods not transported as planned.
- Error in details like GSTIN, vehicle number, or invoice.
- Incorrect consignment information.
Rules for Cancelling
- Can only be canceled within 24 hours of generation.
- Cannot be canceled if the e-Way Bill has been verified during transit.
- Both consignor and transporter can initiate the cancellation.
Step-by-Step Process to Cancel the Bill
- Log into the e-Way Bill portal.
- Navigate to the “e-Way Bill” tab.
- Select “Cancel” option.
- Enter the e-Way Bill number.
- Provide a valid reason for cancellation.
- Confirm and submit the cancellation.
Once canceled, the same e-Way Bill number cannot be used again.
Common Mistakes to Avoid During Cancellation
- Not adhering to the 24-hour timeline.
- Attempting cancellation after goods are verified in transit.
- Providing incomplete or incorrect reasons for cancellation.
Cancelling on time can you maintain clean and compliant documentation and avoid unnecessary scrutiny from tax authorities.
Penalties for Non-Compliance of eWay Bill System
Moving goods without a valid eWay Bill can land you in trouble. You might face:
- A fine of ₹10,000 or the tax sought to be evaded (whichever is higher)
- Detention or seizure of goods and vehicles
To avoid such hassles, always double check that your E-Way Bill is generated and valid before dispatch.
Final Thoughts
The E-Way Bill may seem like just another bureaucratic step, but it’s actually a well-thought-out system designed to streamline logistics and compliance. The eWay Bill system plays a vital role in ensuring smooth, transparent, and compliant goods movement within India and for export shipments. Whether it is generating an individual bill, cancelling one when necessary, or consolidating multiple bills for transportation ease, mastering the process is crucial whether you’re a small trader, a transporter, or part of a large manufacturing unit.
Understanding the nuances of e-Way Bills not only helps businesses avoid legal issues and penalties but also improves supply chain efficiency. Keeping up with E-Way Bill rules ensures smoother deliveries, fewer delays, and no nasty surprises from GST officers.
Always ensure accuracy, timely cancellation if needed, and leverage consolidated e-Way Bills for multiple consignments to optimize your logistics process!
FAQs
An e-Way Bill is an online document that must be carried when goods worth more than ₹50,000 are moved. It is generated by a GST-registered person or a transporter before starting the movement of goods.
Registered suppliers, transporters, and recipients (in case the supplier is unregistered) need to generate an e-Way Bill.
Yes, it is mandatory for the movement of goods valued above ₹50,000 within and across state borders.
The official website for generating an e-Way Bill is ewaybillgst.gov.in.
No, once generated, an e-Way Bill cannot be edited. You must cancel it within 24 hours and generate a new one.
Yes, transporters who are unregistered under GST must enroll on the e-Way Bill portal and obtain a transporter ID to generate e-Way Bills.
If not canceled within 24 hours, the e-Way Bill remains active, and any inconsistencies may lead to penalties if checked during transit.
You must carry the invoice, bill of supply, delivery challan, and the e-Way Bill copy (physical or electronic).
No, it is not mandatory but highly recommended for convenience and smoother logistics operations.