If you’re in the business of exporting goods or services from India, you’ve probably come across something called a Bank Realisation Certificate or BRC. But have you heard of the electronic version — the e-BRC? It’s a game-changer for exporters and plays a big role in claiming government incentives, maintaining compliance, and keeping your paperwork digital and streamlined.
In this blog post, we’re going to break down everything you need to know about e-BRC — what it is, why it’s important, how the process works, and how to check, download, and use it for export incentives. Let’s dive right in.
What is a Bank Realisation Certificate (BRC)
Banks issue a Bank Realisation Certificate (BRC) to exporters. It confirms that the exporter has received payment for a particular export transaction from a foreign buyer. In simple terms, it proves that you got paid for the goods or services you exported.
Exporters usually need this certificate to claim a wide range of export benefits and incentives provided by the Indian government under the Foreign Trade Policy (FTP). These incentives can include duty drawback, GST refunds, interest subsidies, and other financial perks designed to support export businesses.
What Does e-BRC Mean
Now, let’s bring in the digital twist — the e-BRC, short for Electronic Bank Realisation Certificate. As the name suggests, it’s the electronic version of the traditional BRC. The DGFT (Directorate General of Foreign Trade) introduced the e-BRC system in 2012 to digitise and simplify the process of export documentation.
Before this shift, exporters had to manually collect physical BRCs from banks and submit them to the DGFT office. It was time-consuming, prone to errors, and definitely not efficient. But with Digital BRC, the entire system moved online. Banks now submit the payment realisation details digitally, and exporters can access this data directly from the DGFT portal without dealing with piles of paperwork.
Who Issues an e-BRC and How
Authorized Dealer (AD) banks typically the banks through which the exporter receives foreign currency payments, issue the e-BRC. Once they confirm receipt of the payment and verify all required export-related documents, they digitally generate and sign the e-BRC. They then upload the digitally signed document to the DGFT portal.
The key details included in an e-BRC are:
- Exporter’s Name and IEC Code
- Shipping Bill Number
- Invoice Amount and Currency
- Bank Realisation Date
- Amount Realised in INR
- Foreign Buyer Details
- AD Bank Details
Why is eBRC Important for Exporters
The e-BRC isn’t just a fancy digital document. It has real benefits for exporters. Here’s why it matters:
- Proof of Payment/ Export Remittance: It acts as digital proof that you’ve received payment for your export shipment. The validation that the exporter has received payment in foreign exchange for a specific shipment or service is essential for financial, legal, and compliance purposes.
- Claiming Incentives: eBRCs is necessary if you are applying for government incentives under various export promotion schemes. You need it to claim benefits under schemes like MEIS, SEIS, and RoDTEP. Keep in mind, exporters without an eBRC cannot avail any of these benefits.
- GST Refunds: eBRCs are crucial during audits and assessments to prove that international transactions were completed and payments were received. It helps in claiming Integrated GST refunds or Input Tax Credit (ITC).
- Compliance: The eBRC forms part of the documentation required by multiple regulatory bodies like DGFT, RBI, and GST departments. It ensures transparency and reduces the risk of discrepancies during audits or inspections.
- Data Sharing: DGFT shares e-BRC data with several state and central agencies, helping with tax administration and ease of doing business. Not just government agencies, exporters can easily retrieve their certificates online, reducing paperwork and the chances of document misplacement.
How Does the e-BRC Process Work
Understanding the workflow behind e-BRC will help you see how everything connects. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how it all happens:
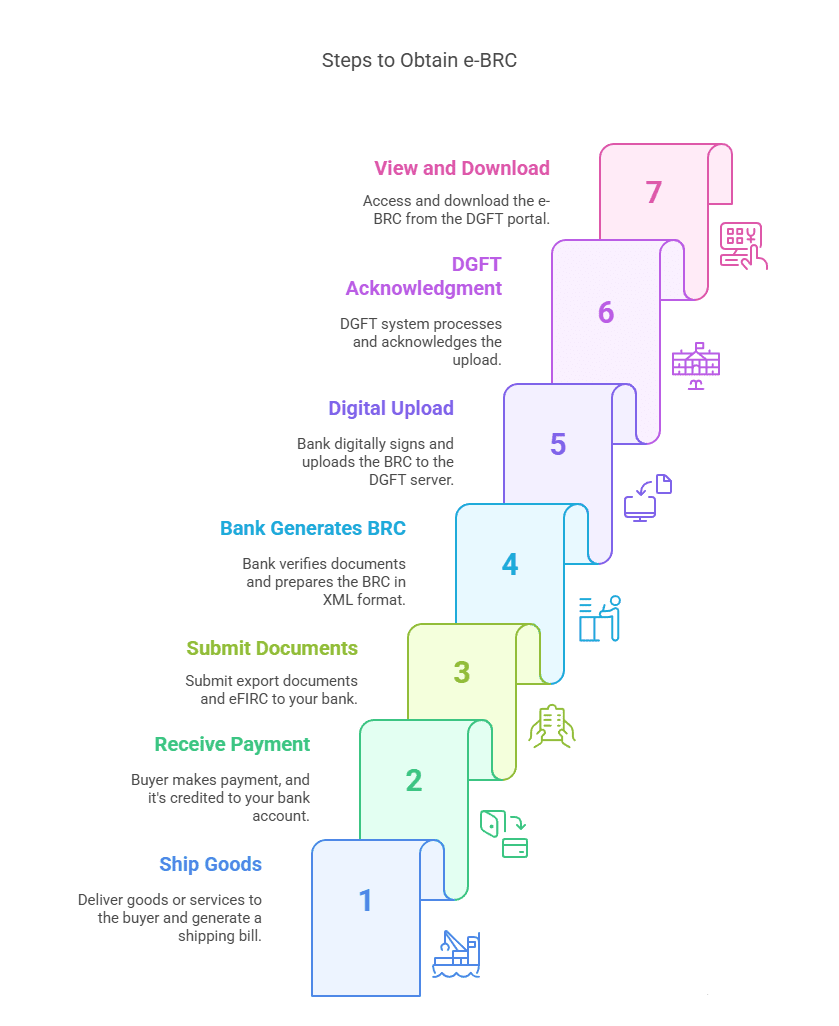
- Shipping the Goods: You ship the goods or deliver the service to your international buyer and generate a shipping bill or invoice.
- Payment Received: Once the buyer makes the payment and it’s credited to your bank account (ideally within 9 months from the date of shipment), you notify your bank.
- Document Submission: You submit supporting export documents and eFIRC (Electronic Foreign Inward Remittance Certificate) to your bank.
- Bank Generates BRC: Your bank verifies the documents, links the payment to your shipping bill, and prepares the BRC in XML format.
- Digital Upload: The bank digitally signs the BRC file and uploads it to the DGFT server.
- DGFT Acknowledgement: The DGFT system processes the file and acknowledges the upload.
- View and Download: You can now view, download, or print the e-BRC from your dashboard on the DGFT portal.
The whole process is digital, paperless, and secure — saving everyone a ton of time and effort.
Steps to Check Your e-BRC on the DGFT Website
Wondering whether your bank has uploaded your e-BRC to the DGFT portal? You can check that in just a few clicks:
- Visit the DGFT website.
- Log in using your credentials.
- Go to My Dashboard > Repositories.
- Under the “Bills Repositories” tab, click “Explore”.
- From the “Select Bill” drop-down list, click on “Bank Realisations (e-BRC)”.
- Enter your desired date range and click “Search”.
You’ll see a list of e-BRCs uploaded by your bank, and you can review the details of each one right there.
How to Download Your Digital BRC
Just follow these simple steps to download your Bank Realisation Certificate:
- Visit the DGFT website.
- Log in using your credentials.
- Go to My Dashboard > Repositories.
- Under the “Bills Repositories” tab, click “Explore”.
- From the “Select Bill” drop-down list, click on “Bank Realisations (e-BRC)”.
- Enter your desired date range and click “Search”. All Electronic Bank Realisation Certificates (e-BRCs) uploaded by your bank will appear on the screen.
- To view a particular e-BRC, select the “Bank Realisation Number”.
- The e-BRC details will pop up.
- Click on the “Print eBRC” option.
- Select the option “Save it as a PDF” for your records to download e BRC.
This document will now serve as proof when applying for export benefits, tax refunds, or for your internal records.
Printing BRC From the DGFT Website
If you’d rather keep a physical copy, printing your BRC is just as easy:
- Follow the same steps listed above for downloading.
- Once you hit Print eBRC, select your printer and get a hard copy.
Make sure your printer is set to high quality if you need to submit the document to any authority.
How to Claim Export Incentives Using an e-BRC
So, you’ve exported your goods or services, the payment has landed in your bank account, and now you’re ready to claim the benefits offered under India’s Foreign Trade Policy. Great! Here’s how the e-BRC plays a big role in helping you get those export incentives.
Let’s break it down step-by-step:
Step 1: Shipping Bill Meets the DGFT System via ICEGATE
Everything starts with your shipping bill, which is generated electronically through ICEGATE—the Indian Customs Electronic Data Interchange platform. Once it’s created, all the shipping bill details are automatically shared with the DGFT system.
Step 2: Link the Dots: Shipping Bill + e-BRC
To claim any export benefit (like MEIS, RoDTEP, etc.), you need to link your shipping bills with their corresponding e-BRCs. This is how the DGFT verifies that the payment for your exports has actually been received.
Step 3: DGFT Calculates the Incentive
Now, when you submit your application, DGFT will match the FOB (Free on Board) value of your goods (from the shipping bill) with the actual payment received (as recorded in your e-BRC). Based on this data, they’ll decide how much incentive you’re eligible for under a DGFT scheme.
Step 4: DGFT Issues the Incentive
If everything matches, the DGFT approves your claim and disburses the incentive.
Pro Tip: Always double-check that your bank has reported the correct realisation value in the e-BRC. If the amount mentioned is lower than what you actually received, ask your bank to fix it. A lower value could mean a lower incentive—or even a rejection of your claim. No one wants that!
Integration with GST and Other Agencies
The e-BRC isn’t just useful for DGFT claims. Its utility stretches beyond into areas like GST compliance. Here’s how:
- Exporters can submit e-BRCs when claiming GST refunds on zero-rated exports.
- e-BRC data is often required when submitting ITC refund applications.
- It serves as a reliable, government-recognized document that validates export transactions in a transparent way.
Also, the DGFT has signed MoUs with several state governments and central agencies for sharing e-BRC data. This inter-agency collaboration means less duplication of work and smoother validation of claims.
e-BRC Portal Update: What’s New
If you’re wondering about changes in the system, here’s a quick update:
- The old e-BRC portal was discontinued in July 2022.
- Banks and exporters now use the new DGFT e-BRC portal.
- AD (Authorised Dealer) banks are required to migrate to this updated platform and continue uploading e-BRCs securely.
So, if you’re still using links or instructions from before mid-2022, it’s time to update your bookmarks and follow the latest process.
Final Thoughts
Whether you’re a seasoned exporter or just getting started, understanding how e-BRCs work is a must. They’re not just another document – they’re your passport to unlocking export benefits, staying compliant, and keeping your business in good shape with government policies.
With everything going digital, using the e-BRC system properly can save you time, avoid hassles, and make your export journey a whole lot smoother. As cross-border trade becomes more digital and streamlined, understanding how to navigate the eBRC process will empower Indian exporters to scale globally with confidence.
FAQs
An eBRC (Electronic Bank Realisation Certificate) is a digital certificate issued by banks in India confirming receipt of foreign exchange payment for exports. It serves as proof of export remittance and is necessary to claim government incentives.
eBRC acts as a legal record of export payment received, making it essential for DGFT, RBI, and GST compliance. Besides export incentives, it is also used for audits and financial reviews.
To generate your eBRC:
1. Register on the DGFT website as an Importer/Exporter.
2. Link your existing IEC or apply for a new one.
3. Go to Services > eBRC > Generate eBRC.
Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the process.
eBRC is required for any business that wants to claim benefits under the Foreign Trade Policy. Once all payments for a shipping bill are received, the exporter can request the bank to close the entry in the EDPMS and generate the eBRC as proof of payment realisation.
e-FIRC confirms receipt of any foreign remittance, while eBRC specifically validates foreign payments for export transactions. eBRC is required for compliance and to claim FTP benefits.
Yes, if you’re selling internationally through Amazon or any platform, an eBRC is needed for every foreign payment to claim export benefits and remain compliant.
Contact your bank immediately. If the eBRC hasn’t been marked as ‘used’ or ‘utilized,’ the bank will cancel it on the DGFT server (status: ‘C’) and issue a new one with a fresh eBRC number (status: ‘F’).
eBRCs don’t expire, but they must be submitted within the timelines specified in FTP schemes to claim export benefits.
Yes, as long as the relevant FTP scheme is active and the claim window is open, you can use valid eBRCs to apply for benefits.
Delays can affect compliance and incentive claims. Follow up with your bank’s forex or trade desk to avoid missing deadlines.