The bill of exchange dates back to the 8th century and was first used by Arab merchants. In modern-day society, bills of exchange are not as popular through domestic transactions. However, businesses use different supply chains and processes to import and export products, which is where the bill of exchange comes into play.
In this article, we will discover what the bill of exchange is, the different types of bills, the benefits involves and the role of bill of exchange in global trading.
What is Bill of Exchange
A bill of exchange is a written document that is created on a purchasing agreement. This can be created by a bank or even an individual trader to help complete transactions. Note, that a bill of exchange isn’t a cheque; it is a document that helps pay for goods and services with international trades.
Let’s look at an example: A US business looks to pay stock from a business in India. The payment is $20,000 which is around 1,650,000 Indian rupees. The Indian company creates a bill of exchange which includes the payment price and due date of the payment. This is then sent over to the US company, whereby the authorized person signs the BOE, accepting the payment.
Information Included in BOE
The bill of exchange includes the amount to be paid, due date, names of payer and payee, and signatures, making it a binding promise to settle the stated amount.
- Title
- Amount of money that needs to be paid
- As of: This is known as the payment’s due date
- Identification number: This is for tracking the document and payments from the accounts.
- Payee: This person that would receive the payment
- Simple Signature
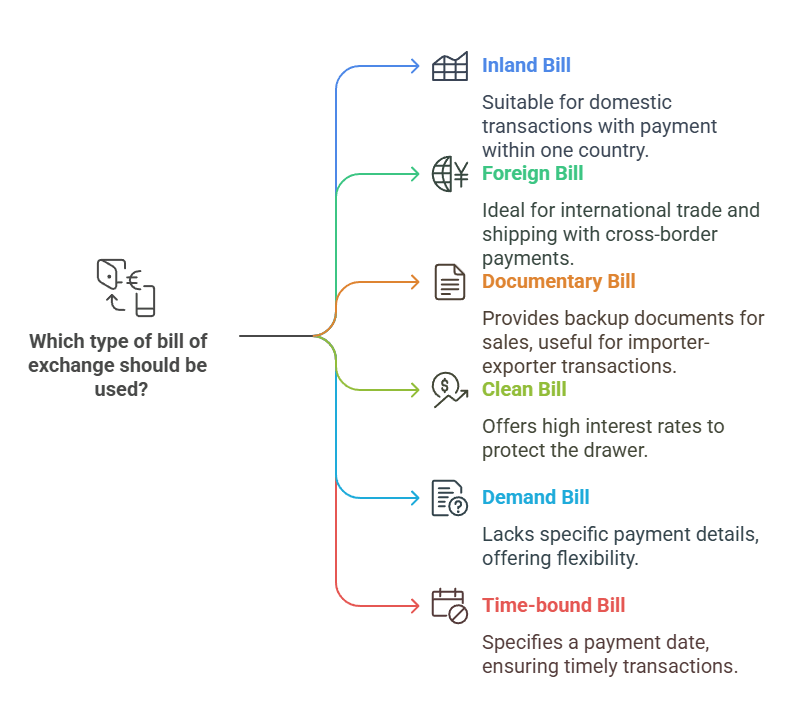
Six Types of Bill of Exchange in Export
There are six main types of bills of exchange which are used with business and purchases:
- Inland Bill: This focuses on payment methods which can only be made in one country.
- Foreign Bill: These can be drawn and paid within different countries; this is usually for international trade or international shipping prices.
- Documentary Bill: This bill offers backup documents which shows the price of the sale. This is usually a transaction between an importer and exporter.
- Clean Bill: This type of bill offers high interest rates in order to protect the drawer of the sale.
- Demand Bill: This bill doesn’t contain a date or specifics of a payment.
- Time-bound Bill: This type gives the drawee a specific date to pay the prices provided.
Conditional vs Unconditional Bill of Exchange
| Aspect | ✅ Unconditional Format | ❌ Conditional Format |
|---|---|---|
| Nature of Order | Absolute and binding | Dependent on a condition |
| Legal Validity | Valid bill of exchange | Invalid as per NI Act |
| Certainty of Payment | Guaranteed | Uncertain |
| Transferability | Can be endorsed/transferred | Cannot be legally negotiated |
| Example Format (Text) | “Pay ₹50,000 to ABC Ltd.” | “Pay ₹50,000 to ABC Ltd. after delivery of goods.” |
| Effect in Business | Trusted in trade & finance | Creates legal ambiguity |
Benefits of Bill of Exchange
Bills of exchange offer a wide range of benefits, especially for accounting, trade, and payment purposes. Here are some key advantages:
1. Legal Protection and Security
- Bill of exchange are legally recognized financial instruments globally, ensuring protection for all parties involved.
- These documents serve as legally binding agreements that help businesses secure payments, even in international transactions.
- They clearly state the amount to be paid, the payee, the drawee, and the due date, preventing disputes and misunderstandings.
2. Facilitates Credit Transactions
- Businesses can use bills of exchange as a credit instrument, allowing buyers to purchase goods on credit and pay later.
- Sellers can receive assurance of future payment without requiring immediate cash transactions.
- This helps businesses manage cash flow effectively and maintain operational efficiency.
3. Transferability and Negotiability
- A bill of exchange is a negotiable instrument, meaning it can be transferred from one party to another.
- The holder can endorse and transfer the bill to another party, making it a flexible tool for trade, export and finance.
- This feature allows businesses to settle debts efficiently without requiring direct cash payments.
4. Discounting and Liquidity Management
- The payee (creditor) can opt to discount the bill with a bank or financial institution to receive immediate funds.
- This enables businesses to access working capital without waiting for the bill’s maturity date.
- Discounting bills of exchange is a common practice in trade financing to maintain smooth financial operations.
5. Reduces Risk of Non-Payment
- Since a bill of exchange is a written, signed, and legally binding document, it reduces the risk of non-payment.
- In case of default, legal action can be taken against the drawee to recover the amount due.
- This gives assurance to sellers, exporters, and lenders in commercial transactions.
6. Promotes International Trade
- Bills of exchange are widely used in international trade, enabling cross-border transactions with reduced risks.
- They help exporters secure payments from foreign buyers, ensuring seamless trade relationships.
- Many financial institutions provide additional support, such as trade finance and guarantees, based on bills of exchange.
7. Involvement of Drawee in Payment
- The drawee is the party who is required to make the payment specified in the bill of exchange.
- Once the drawee accepts the bill, they become legally bound to pay the specified amount on the due date.
- The drawee’s acceptance adds credibility to the transaction and ensures that the payee receives their due payment.
8. Encourages Financial Discipline
- By setting a definite payment timeline, bills of exchange promote timely payments and financial discipline.
- Businesses can plan their accounts receivable and payable efficiently, reducing financial uncertainty.
- This structured payment system helps maintain good business relationships and trust among parties while exporting products.
Lifecycle of a Bill of Exchange: From Acceptance to Protest
A bill of exchange is a vital financial instrument used in trade, and understanding its lifecycle is crucial. Once issued, the acceptance of the bill by the drawee signifies their agreement to pay the specified amount at a future date. The duration until this payment is due is known as the tenor of the bill, and the actual date when the payment must be made is called the maturity date.
If the drawee fails to honor the bill by the maturity date, it results in the dishonour of the bill. In such cases, the holder may initiate a formal protest of the bill, which is a legal declaration typically certified by a notary public. To support this process, noting charges are incurred, representing the cost of recording the dishonour and protest. These procedures protect the rights of the holder and help maintain accountability in domestic and international trade.
What is the Role of Bill of Exchange in Global Shipping
A bill of exchange plays a reliable role within the global shipping industry in helping with international transactions.
Here are six reasons how the BOE and international shipping works together:
1. Negotiable Instrument
Bills of exchange are able to help transfer payments like banks or financial institutions.
2. Payment Information
Bills of exchange also help to provide reliable payment information and terms between both the buyer and the seller. The information includes a due date, currency and the payment amount. If failed to pay, the bill of exchange can be enforced to give the seller a legal claim.
3. Secure Payment Transfers
They also help to provide a secure system where sellers can provide information on the payment sum for buyers. This provides an extra level of protection.
4. Lowers Credit Risk
Sellers may need to deal with international shipping and unfamiliar buyers. This document ensures that sellers can reduce their credit risk, as buyers are obligated to pay once they have purchased an item or product.
5. Shipping Information
Bills of exchange are used alongside shipping documents. These documents are usually collected and managed by banks to help buyers receive their shipping products. This ensures all payment terms and transfers are done correctly.
6. Trade Acceptance
When selling products internationally, international shipping companies from India need to consider legal information and currencies. Bills of exchanges help with payment processes and ensure international transactions are done smoothly.
Example of Unconditional Bill of Exchange (Valid)
Date: 09 May 2025
Place: MumbaiTo,
Mr. Raj Malhotra,
47 Business Park, Delhi.Pay ₹1,00,000 (Rupees One Lakh only) to the order of M/s J.K. Traders three months after date.
Sd/- Rohit Agarwal (Drawer)
Example of Conditional Bill of Exchange (Invalid)
Date: 09 May 2025
Place: MumbaiTo,
Mr. Raj Malhotra,
47 Business Park, Delhi.Pay ₹1,00,000 to M/s J.K. Traders only if the goods are found satisfactory.
Sd/- Rohit Agarwal (Drawer)
Conclusion
It is a clear bill of exchange document are vital for shipping companies to ensure customers are able to pay for their orders and sellers are guarantee of payment. However, if a customer fails to pay due to the bill of exchange, sellers are able to take legal action against this. This document is used during international trading to protect small businesses and ensure all contract information is followed.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Bill of Exchange
A bill of exchange is a legally binding financial instrument that directs one party (the drawee) to pay a specific sum of money to another party (the payee) at a predetermined date. It is commonly used in trade and financial transactions.
The three main parties involved in a bill of exchange are the drawer, drawee, and payee. The drawer is the individual or entity that issues the bill and anticipates receiving the payment. The drawee is the person or organization upon whom the bill is drawn and who is obligated to pay the specified amount. Lastly, the payee is the recipient of the payment, who is often the same as the drawer but can also be a third party depending on the terms of the transaction.
The drawer writes the bill, specifying the amount to be paid and the due date. The drawee accepts it by signing, agreeing to make the payment. The payee (or the holder of the bill) presents it for payment on the maturity date.
Yes, a bill of exchange is a legally binding document. If the drawee fails to pay, the drawer can take legal action to recover the amount.
Yes, a bill of exchange is a negotiable instrument, meaning it can be endorsed and transferred to another party. This allows businesses to use it for trade financing.
If a bill is dishonored (not paid on the due date), the holder can take legal action against the drawee. The bill may also be noted and protested for legal enforcement.
A bill of exchange is an order to pay, while a promissory note is a promise to pay. In a bill of exchange, the drawer orders the drawee to pay the payee, whereas in a promissory note, the issuer directly promises to pay the recipient.
Yes, the holder can discount the bill with a bank or financial institution to receive immediate cash before the maturity date. This helps businesses maintain cash flow.
Yes, bills of exchange are widely used in international trade as a secure method of payment. They provide assurance to exporters and facilitate smooth transactions between buyers and sellers across borders.
The drawee is the party responsible for making the payment. Once they accept the bill, they are legally bound to pay the specified amount on the due date.